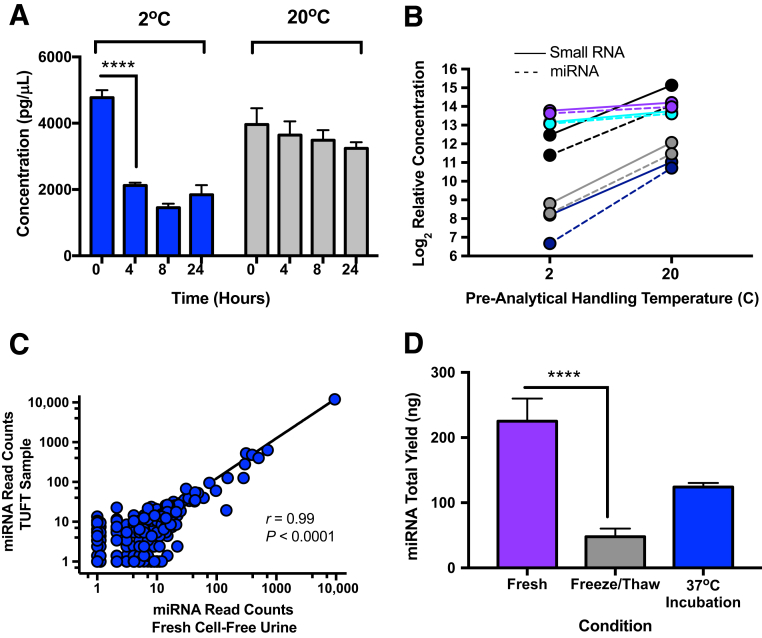
Figure 2.
Different pre-analytical handling conditions result in altered miRNA recovery from urine extracellular vesicles (EVs). Whole urine was equilibrated at 2°C (on ice) or 20°C for up to 24 hours. At the conclusion of each time point, two low-speed centrifugations (200 × g and 1000 × g; 10 minutes each) were performed to eliminate cells and cell debris. miRNA concentrations were measured via the Agilent 2100 Bio-Analyzer. A: Recovery of miRNAs from urine at 2°C was markedly decreased over time compared with immediate processing. B: Equilibration of urine at 20°C resulted in greater recovery of miRNA compared with a cold (2°C) pre-analytical handling condition. Each time point was run in triplicate from healthy donors. Because of the large volume of biofluid needed for the time course (TC) study, one healthy donor sample was used for 2the °C TC and another healthy donor was used for the 20°C TC. In addition, small RNA and miRNA recovery was measured from multiple donors after sample equilibration at 2°C or 20°C for 4 hours. C: Less small RNA and miRNA is recovered from all donors when samples were held at 2°C compared with 20°C. Each of the five donors is represented by a different color, with small RNA shown as a continuous line and miRNA represented by a dashed line. RNA quantity is plotted as log2 relative concentration because of the variability of RNA yield among donors. Each line is an individual sample. Graph represents directional change across the study population. NanoString nCounter miRNA assay reveals good correlation of miRNA read counts between fresh urine sample and total urine with a one-time freeze/thaw (TUFT) from the same donor (patient with cystic fibrosis) with a normalized input quantity. D: miRNA recovery is partially rescued when precipitate is solubilized at 37°C for 5 minutes from freeze/thaw samples. Each time point was run in triplicate from one healthy donor. Graph shown is representative of multiple experiments. Data are expressed as means ± SD (A and D). n = 5 donors (B). ∗∗∗∗P < 0.0001 (Tukey-Kramer honestly significant difference).