Figure 3.
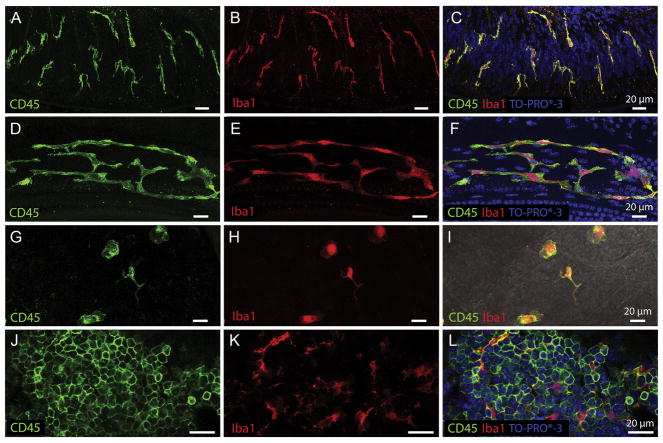
Tissue macrophages display different morphologies in distinct cochlear partitions. A–C. Osseous spiral lamina macrophages residing among the peripheral nerve bundles of ganglion neurons. Under steady-state conditions, osseous spiral lamina macrophages present with a branched, dendritic morphology as revealed by CD45 (A) and Iba1 (B) immunolabeling. They are oriented radially toward the lateral edge of the osseous spiral lamina. To provide further context for immune cell analysis, tissues were counter-stained with TO-PRO®-3 (C). D–F. Steady-state BM-macrophages in the middle and basal cochlear region present as a network of long and thin curvilinear cells that follow the natural anatomic curve of the basilar membrane. BM-macrophages strongly express CD45 (D) and Iba1 (E) immunoreactivity. G–I. Macrophages on the luminal surface of the scala tympani in the basal turn of a naive cochlea. Under resting conditions, these cells present with a variety of morphologies (amoeboid to branched), are sporadically located among non-immune cells on the surface of the scala tympani, and possess both CD45 (G) and Iba1 (H) immunoreactivity. A merged image with CD45 and Iba1 colocalization can be seen in DIC view (I). J–L. CD45 (J) and Iba1 (K) immunohistochemistry performed on bone marrow harvested from the cochlear bony shell shows many small, rounded and undifferentiated leukocytes with very strong CD45 immunoreactivity (J). These small less-differentiated cells do not express the macrophage-specific protein Iba1. However, among the undifferentiated bone marrow leukocytes reside globular, branched, fully differentiated macrophages that express strong Iba1 immunoreactivity (K) indicating that only mature macrophages, but not less-differentiated leukocytes, express Iba1. CD45 and Iba1 colocalization with TO-PRO®-3 nuclear labeling can be seen in panel L.