Figure 1.
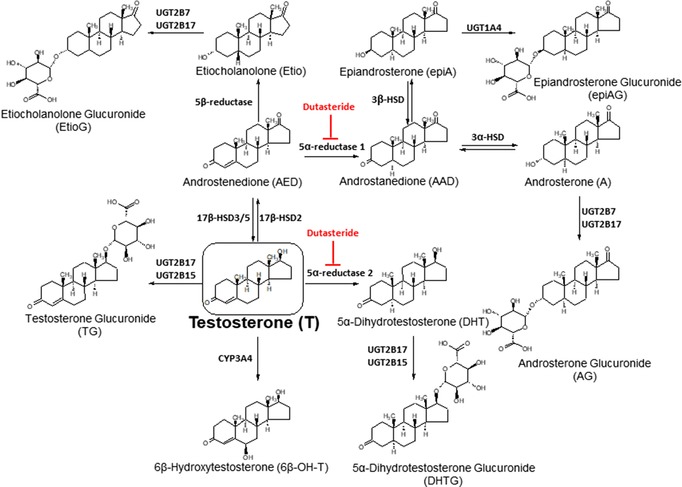
Major metabolite pathways of testosterone (T) disposition in vivo. All these metabolites were quantified by targeted metabolomics analysis. Testosterone is conjugated by UGT2B17 and UGT2B15 to testosterone glucuronide (TG). Testosterone is also converted to dihydrotestosterone (DHT), AED, and 6β‐hydroxytestosterone (6β‐OH‐T) by 5‐AR2, 17β‐HSD2, and CYP3A4, respectively. AED is then metabolized to the number of sequential metabolites, i.e., etiocholanolone (Etio), androstanedione, androsterone (A) and epiandrosterone (epiA). Both A and Etio are conjugated by UGT2B7 and UGT2B17 to A glucuronide (AG) and Etio glucuronide (EtioG), whereas epiA is glucuronidated by UGT1A4 to epiA glucuronide. All these metabolites (except epiA, epiAG, and 6β‐OH‐T) were quantifiable in both 200 and 800 mg dose in the following relative order: AG>TG>EtioG>AED>A>T>DHT>Etio. Dutasteride is a dual inhibitor of 5‐AR1 and 5‐AR2. Sulfate conjugates were not analyzed in this study.
