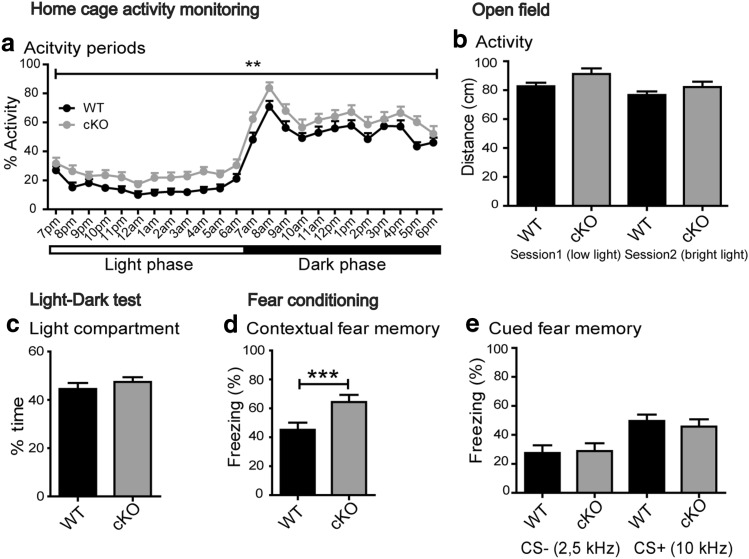
Fig. 3.
Bsn cKO mice display increased contextual fear memory. a Analysis of home cage activity in WT (N = 20) and Bsn cKO (N = 19) mice suggests normal circadian rhythm with increased locomotion during the dark phase. Activity values of cKO mice are generally increased as compared to WT mice. b In an open field test WT and cKO mice show similar levels of exploratory activity under both low light and bright light illumination (distance explored) (WT: N = 24; cKO: N = 19). C Anxiety levels are unchanged in cKO mice as indicated by the percentage of time spent in light chamber during the light–dark test (WT: N = 12; cKO: N = 10). D Increased freezing towards the shock context is observed in cKO mice indicating an enhanced contextual fear memory. e By contrast no genotype difference is evident in the conditioned fear response towards the auditory tones in neutral context; both groups furthermore clearly differentiate the neutral acoustic stimulus (CS−) and conditioned acoustic stimulus (CS+) (WT: N = 13; cKO: N = 11). All values are mean ± SEM; **p ≤ 0.01, ***p ≤ 0.001, two-way repeated measures ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test (a–e), Mann Whitney U test (c)