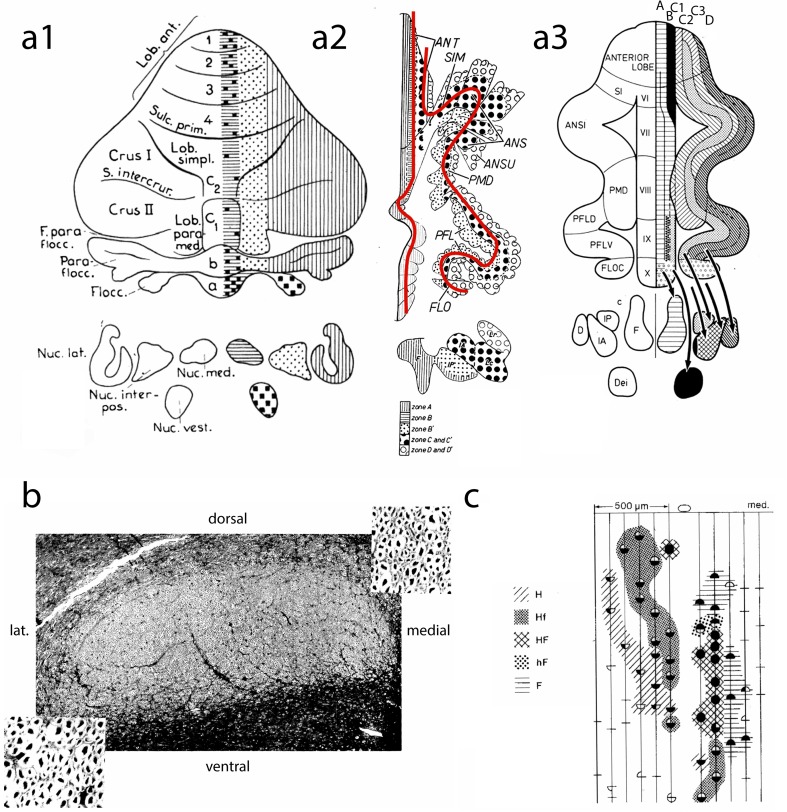
Fig. 2.
a1 Diagram of the corticonuclear projection of the cerebellum, showing the vermal, intermediate, and lateral zones of Jansen and Brodal [24]. Nomenclature of the lobules according to Bolk [25]. a2 Diagram of the flattened cerebellar cortex of the cat showing the corticonuclear projection (after Voogd [26]). The red lines indicate the direction of the folial chains of vermis and hemisphere. a3 Corticonuclear projection shown in diagrams of the flattened cerebellar cortex of the cat from Groenewegen et al. [19]. b Superior cerebellar peduncle of the cat, Häggqvist stain. Note small myelinated fibers in the medial third and coarse fibers in lateral two-thirds [after 24]. c Microzones with different climbing fiber inputs in the B zone of the cerebellum of the cat. Stimulation of the ipsilateral and contralateral ulnar and sciatic nerves results in Purkinje cells with similar responses in microzones as indicated by different hatching and stippling: H (hindlimb), Hf (mainly hindlimb), HF (hind- and forelimb), hF (mainly forelimb), F (forelimb), after Andersson and Oscarsson [27]. ANS, ANSI ansiform lobule; ANSU ansula; D dentate nucleus; Dei Deiters nucleus; F fastigial nucleus; F. parafloc parafloccular fissure; FLO, FLOC flocculus; IA anterior interposed nucleus; IP posterior interposed nucleus; Lc. Lateral nucleus pars convexa; Lob. Paramed paramedian lobule; Lob.ant, ANT anterior lobe; Lob.simpl simple lobule; Lr, lateral nucleus pars rotunda; Nuc.interpos interposed nucleus; Nuc.lat lateral nucleus; Nuc.med. medial nucleus; Nuc.vest. vestibular nucleus; Parafloc paraflocculus; PFL(D,V) paraflocculus (dorsalis, ventralis); PMD paramedian lobule; S.intercrur intercrural sulcus; SIM, SI primary fissure simplex lobul; Sulc.prim