Fig. 3.
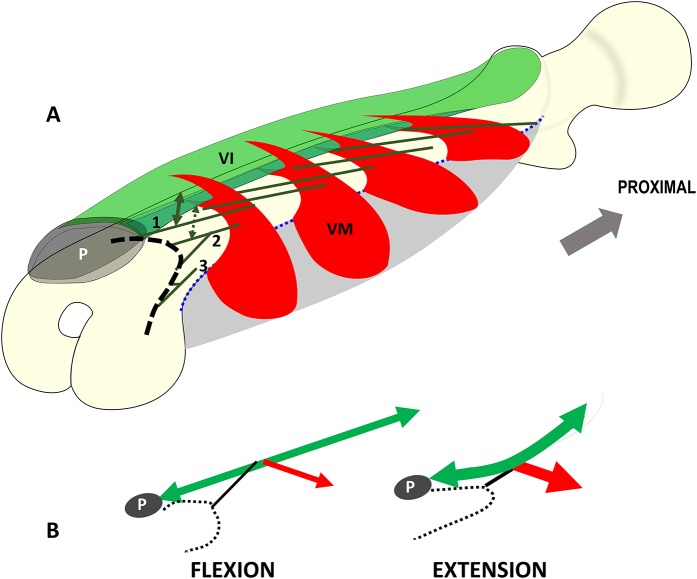
Figs. 3-A and 3-B Schematic drawings showing the anatomy and mode of operation of the interacting muscle complex consisting of the articularis genus, vastus intermedius (VI), and vastus medialis (VM). Fig. 3-A Schematic illustration depicting the hammock-like origin (gray) and the fleshy clip-like double-insertion of the vastus medialis units (red) into the entire vastus intermedius aponeurosis (green). The blue dotted line corresponds to the origin of the vastus medialis at the medial lip of the linea aspera. The vastus medialis clamps the vastus intermedius aponeurosis like a clip holding a sheet. The deep layer of the vastus intermedius (green lines) corresponds with the muscle bundles that continue as the articularis genus to the knee joint. The superficial layer of the vastus intermedius contributes to the layers of the quadriceps tendon and finally inserts into the base of the patella (P). In the present study, the superficial articularis genus muscle bundles (indicated by the number 1) always originated from both the anterior surface of the femur and the vastus intermedius (double arrows). The deep articularis genus muscle bundles (indicated by the number 3) arose solely from the femur. The intermediate articularis genus muscle bundles (indicated by the number 2) always arose from the anterior surface of the femur. However, in 60% of the specimens, muscle fibers also originated from the vastus intermedius aponeurosis. All muscle bundles of the articularis genus inserted into the synovial membrane of the joint capsule and the suprapatellar bursa (black dashed line). Fig. 3-B Schematic illustration depicting the mode of operation of the muscle complex consisting of the articularis genus (black lines), vastus intermedius (green double arrows), and vastus medialis (red arrows). As a derivative of the vastus intermedius, the articularis genus consists of a few muscle bundles that arise from the deep part of the vastus intermedius. Therefore, the articularis genus does not act as an independent entity. The muscle bundles of the articularis genus connect with the neighboring vastus intermedius and vastus medialis. With their support, the articularis genus retracts or elevates the suprapatellar bursa (black dotted lines) during extension of the knee, preventing entrapment of the bursa between the patella (P) and the femur.