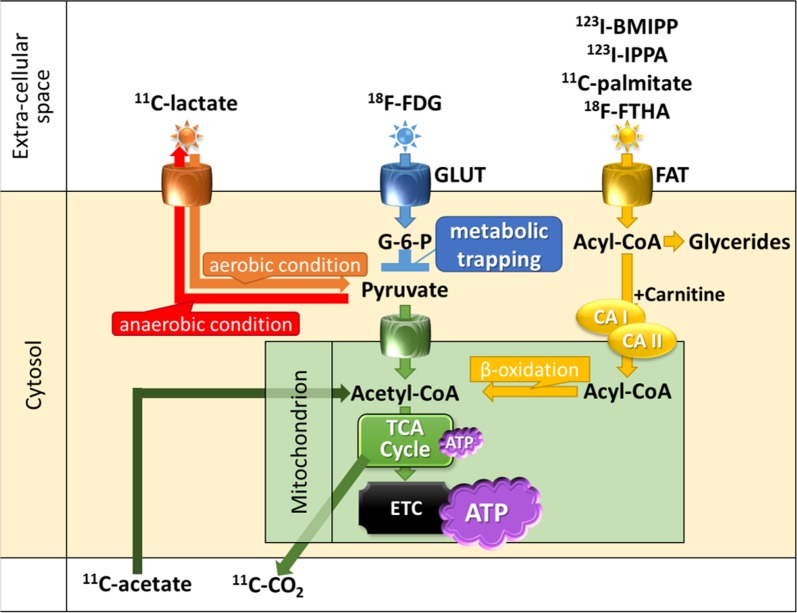
Figure 6.
Tracers for assessing cardiac energy metabolism 18F-FDG is a glucose analog in which the oxygen in position C-2 is replaced with 18F. 18F-FDG is actively transported into the cell mediated by GLUT in the same way as glucose. Once inside the cell, glucose and 18F-FDG are phosphorylated by hexokinase. Phosphorylated glucose (G-6-P) continues along the glycolytic pathway for energy production. However, 18F-FDG-6-phosphate cannot enter glycolysis and is trapped intracellularly in a condition known as “metabolic trapping.” GLUT, glucose transporter; G-6-P, glucose-6-phosphate; FDG, 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose; FDG-6-P, 18F-FDG-6-phosphate