Fig. 2.
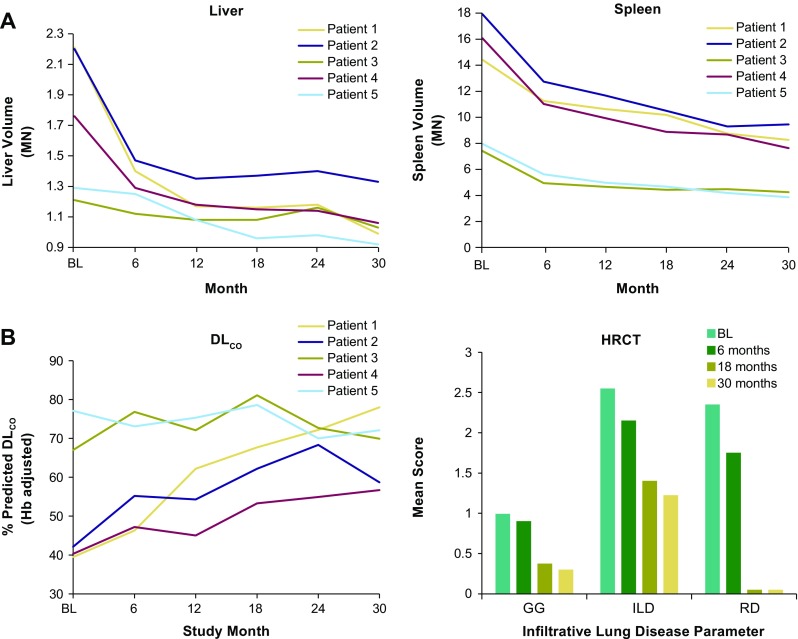
Assessment of olipudase alfa on liver and spleen volume and lung disease. (a) Liver and spleen volumes were calculated by integrating cross-sectional magnetic resonant images and expressed as multiples of normal (MN) where normal spleen volume (L) was assumed to be 0.2% of body weight and normal liver volume (L) to be 2.5% of body weight. (b) Lung disease. By-patient percent predicted DLco, adjusted for hemoglobin (Hb), at baseline and during treatment were calculated from observed values for male and female patients (Crapo and Morris 1981, Macintyre et al 2005). Degree of severity: 80% = lower limit of normal; >60%–79% = mild decrease; 40%–60% = moderate decrease; <40% = severe decrease. HRCT assessment of infiltrative lung disease at baseline and during treatment with olipudase alfa included ground glass appearance (GG), interstitial lung disease (ILD), and reticulonodular density (RD) scored on a 4 point system where 0 = No interstitial lung disease; 1 = Mild (affecting 1–25% of the lung volume); 2 = Moderate (affecting 26–50% of the lung volume); 3 = Severe (affecting 51–100% of the lung volume)
