Figure 1.
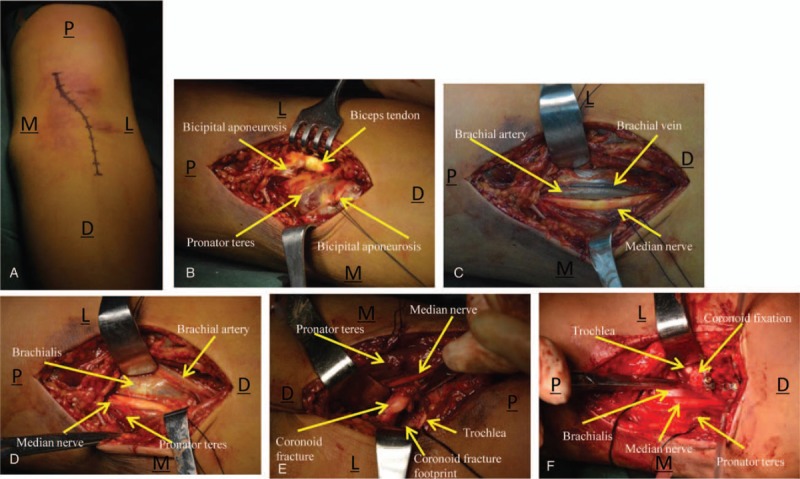
(A) A single “S”-curved incision was made along the medial border of the biceps and extended along the midline of the forearm. (B) Bicipital aponeurosis was exposed and incised. (C) Image depicts the brachial artery, brachial vein, and median nerve. (D) Brachial muscle insertion was exposed through an interval created between the brachial artery and median nerve. (E) After dissection of a small part of the lateral insertion of the brachial muscle, the coronoid fracture fragments are observable. (F) Image shows accurate reduction and rigid fixation of the coronoid process, with an intact brachialis. M = medial, L = lateral, P = proximal, D = distal.
