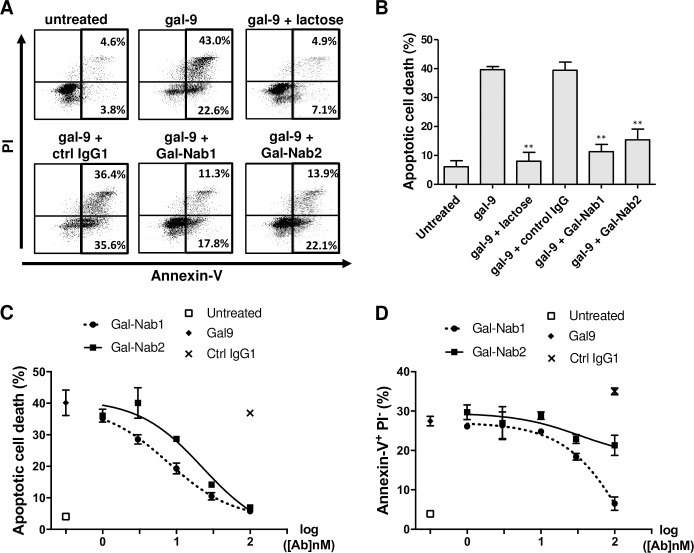
Fig 2. Anti-gal-9 mAbs efficiently neutralize gal-9-induced apoptosis in primary T cells.
CD3+ T-cells were isolated from healthy donors, activated by a combination of CD3/CD28 antibodies and treated or not with gal-9 (gal-9S; 40 nM) alone or in combination with lactose (5 mM), control isotype mAbs (ctrl IgG1) or anti-gal-9 mAbs (Gal-Nab1 and Gal-Nab2) at 67 nM (i.e. 10 μg/mL). After 36 h, they were subjected to annexin-V/PI staining and flow cytometry analysis. A. Examples of flow cytometry plots for purified CD3+ cells from one donor. B. Synthesis of data from 3 similar experiments made with CD3+ cells from 3 donors. C and D. Dose-response curves for apoptotic cell death (annexin-V+ PI+) (C) or PS translocation (annexin-V+ PI-) (D) in activated CD3+ cells treated for 36h with gal-9 combined with increasing concentrations of Gal-Nab1 and Gal-Nab2 (0.3 to 100 nM). Empty squares indicate the percentages obtained in conditions without gal-9. Black crosses indicate the percentages obtained with isotype control IgG1 mAbs used at maximal concentration (100 nM). Data are presented as means ± SEM of three independent experiments made with three distinct donors.