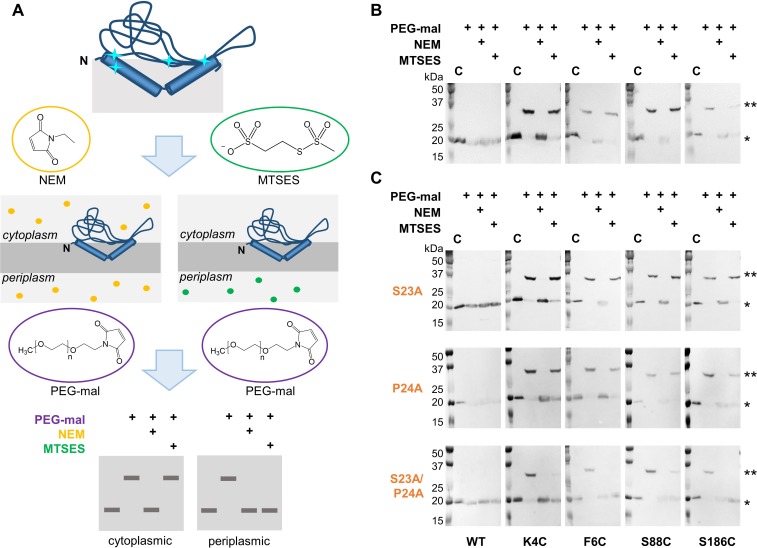
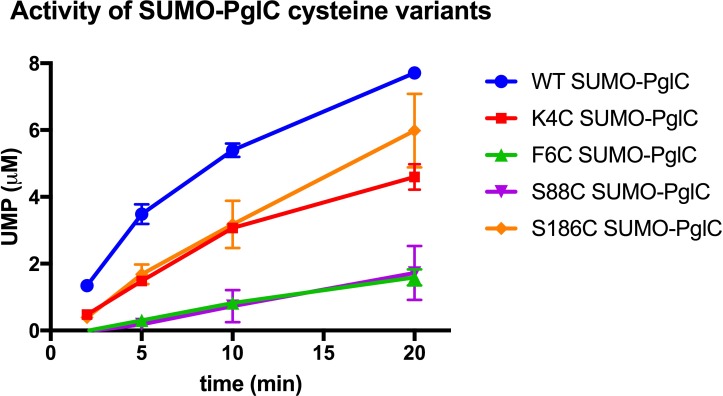
Figure 2. Ser23 and Pro24 act together to enforce the reentrant PglC topology.
(A) Schematic representation of SCAM analysis used to assess the topology of wild-type PglC and variants. Cyan starbursts (top) indicate the location of unique cysteines introduced into PglC. (B) SCAM analysis of wild-type PglC topology (* = native PglC; ** = PglC labeled with PEG-mal; C = control, no PEG-mal labeling). (C) SCAM analysis of S23A, P24A and S23A/P24A PglC variant topologies. All SCAM experiments were performed in duplicate or more. Representative Western blots are shown.