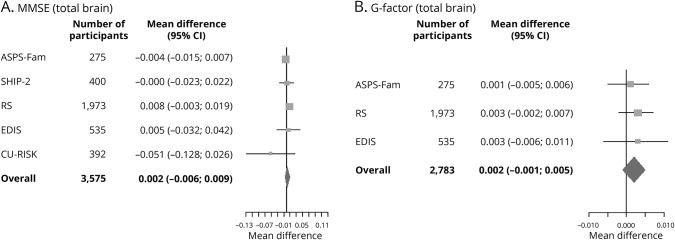
Figure 1. Forest plots of the association of total brain ePVS counts with (A) MMSE score and (B) G-factor.
Effect estimates adjusted for age, sex, ethnicity, education, systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, total cholesterol, type 2 diabetes mellitus, lacunes, white matter hyperintensities, intracranial volume, gray matter volume, and white matter volume for the association between total enlarged perivascular spaces (ePVS) counts and Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) and general fluid cognitive ability factor (G-factor). ASPS-Fam = Austrian Stroke Prevention Family Study; CI = confidence interval; CU-RISK = Chinese University of Hong Kong–Risk Index for Subclinical Brain Lesions in Hong Kong; EDIS = Epidemiology of Dementia in Singapore; RS = Rotterdam Study; SHIP = Study of Health in Pomerania.