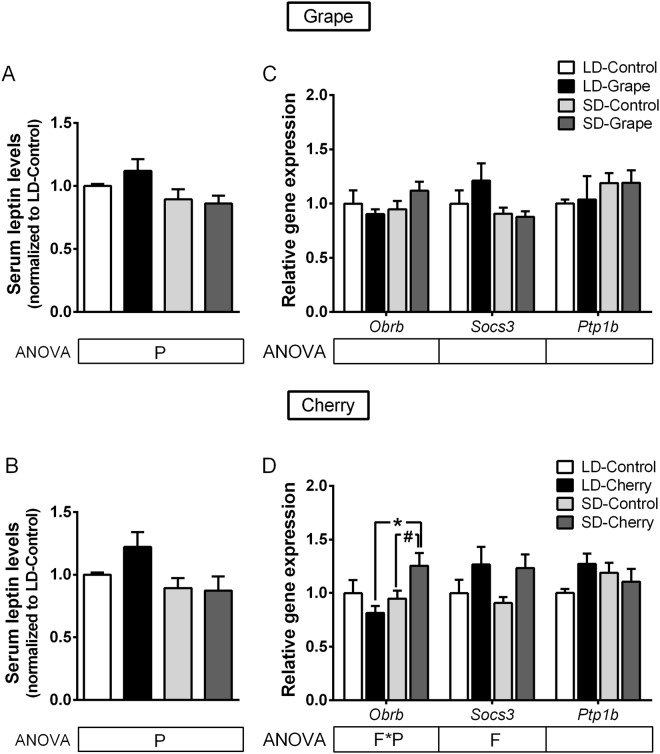
Figure 2.
Effect of photoperiod and seasonal fruit supplementation on hypothalamic leptin sensitivity in non-obese animals. (A,B) Serum leptin concentrations were measured in animals fed standard chow diet + vehicle or 100 mg/kg of lyophilized grapes or cherries for a 10-week-period and submitted to long-day (LD) or short-day (SD) photoperiods. (C,D) Gene expression of long-form leptin receptor (Obrb) and negative regulator molecules Socs3 and Ptp1b were analyzed by quantitative PCR. Values were normalized against LD-vehicle group for leptin concentration and gene expression. Data represent mean ± SE (n = 6). P, photoperiod effect; F, fruit effect; F*P, interaction of photoperiod and fruit treatment assessed by two-way ANOVA (P < 0.05). *Effect of photoperiod in fruit-treated groups; #Effect of fruit in photoperiod group determined by Student’s t test (P < 0.05).