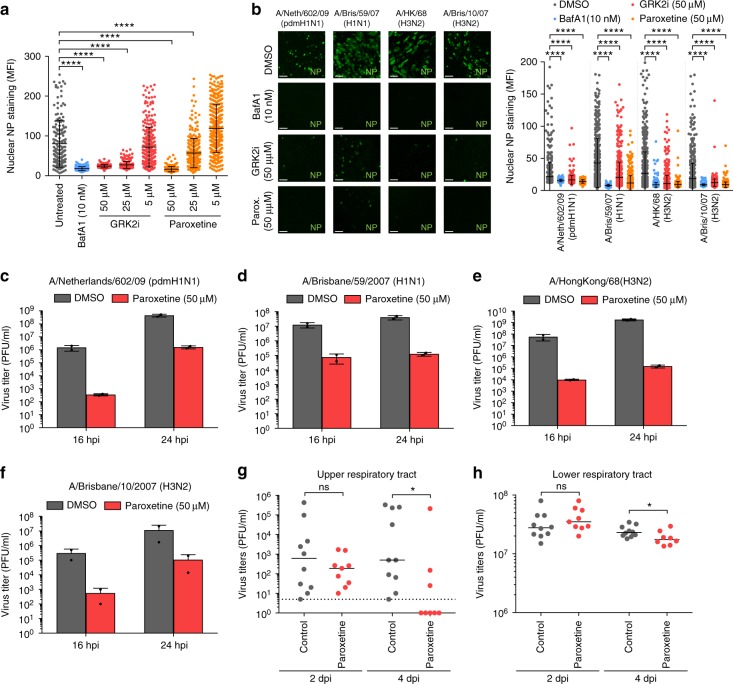
Fig. 5.
IAV replication can be limited by the use of GRK2 inhibitors in human airway cultures and in mice. a A549 cells were treated for 1 h with the indicated amounts of the different compounds and infected on ice with IAV A/WSN/33 (H1N1) at an MOI = 5 PFU/cell. Cells were incubated at 37 °C for 3 h in presence of the inhibitors, fixed and stained for viral nucleoprotein (NP, green) and nuclei (blue). The distribution of NP at the different time-points was analyzed by confocal microscopy and mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) in the cell nuclei (n > 200) was quantified using ImageJ. One representative out of four independent experiments is shown. Statistical significance was determined by unpaired t-test. b Fully differentiated human airway epithelial (HAE) cultures were infected with the indicated human IAV strains (107 PFU/well) in presence of the indicated compounds. Cells were processed and NP nuclear staining was quantified as described in (a). Scale bar corresponds to 40 µm. One representative out of at least two independent experiments is shown. c–f HAE cultures were infected with the indicated human IAV strains (1000 PFU/well) in presence or absence of paroxetine. At the indicated times post-infection, supernatants were harvested and virus titers were determined by plaque assay. For a–f, error bars represent standard deviation and statistical significance was determined by unpaired t-test. g, h Virus titers in the upper respiratory tract (URT) and lower respiratory tract (LRT) of mice treated with solvent (gray) or paroxetine (red) and infected with A/Netherlands/602/2009 (pdmH1N1) for 2 and 4 d pi are depicted (two independent experiments, n ≥ 8 per group). Statistical significance was determined using non-parametric two-tailed Mann–Whitney test. For all panels, ns (non-significant) = P > 0.05; *P ≤ 0.05; **P ≤ 0.01; ***P ≤ 0.001; ****P ≤ 0.0001