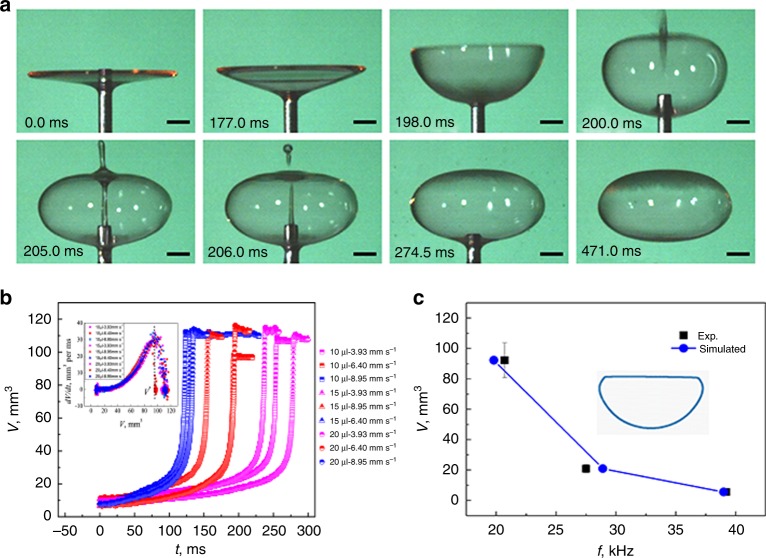
Fig. 4.
Resonance mechanism for bubble formation of acoustically levitated drops. All the drops were SDS drops at CMC. a Snapshots showing that dragging a needle positioned at the center of the film caused it to buckle, resulting in abrupt inflation and bubble formation. Each scale bar represents 1 mm. b Cavity volume V as a function of dragging time for liquid films of different initial volumes (10, 15 and 20 µL) and different dragging rates (3.93–8.95 mm/s). Similar abrupt volume inflation was observed corresponding to the same critical cavity volume V* (see inset). c V* as a function of working frequency of the levitator; squares are experiment, circles are simulation. Inset image illustrates the contour line of the cavity corresponding to the maximum inflation rate for 20.7 kHz