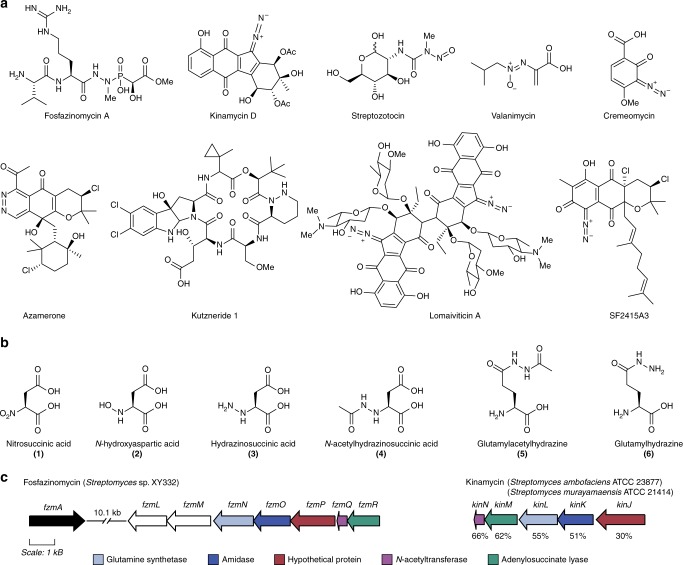
Fig. 1.
Structures and biosynthetic gene clusters of fosfazinomycin and kinamycin. a Structures of a select group of N–N bond-containing natural products. b Structures of the biosynthetic intermediates discussed in this study. c Selected segments of the biosynthetic gene clusters of fosfazinomycin and kinamycin that encompass the genes discussed in this study. The five conserved genes in the two clusters are colored based on annotations of their gene products using BLAST analysis: glutamine synthetase (blue-gray), amidase (dark blue), hypothetical protein (red), N-acetyltransferase (purple), and adenylosuccinate lyase (green). The amino acid identities between the homologous enzymes from the fzm cluster from Streptomyces sp. XY332 and the kin cluster from Streptomyces murayamaensis ATCC 21414 (FzmN/KinL, FzmO/KinK, FzmP/KinJ, FzmQ/KinN, and FzmR/KinM) are indicated below the kin cluster. fzmL and fzmM, which encode enzymes responsible for forming nitrous acid from aspartic acid, are colored in white