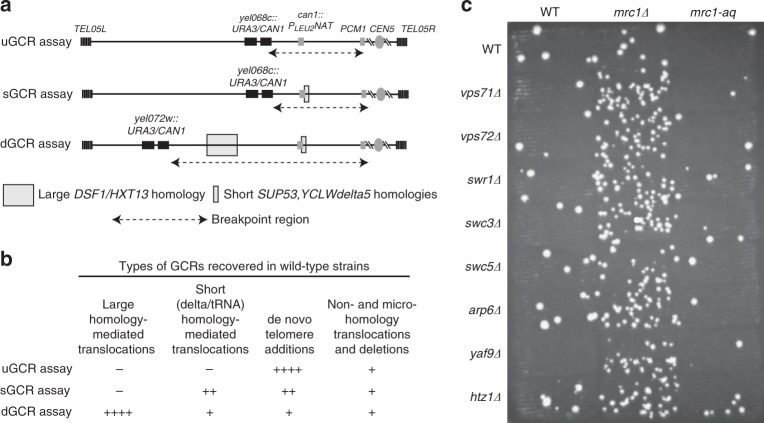
Fig. 1.
A mrc1Δ mutation causes increased GCRs when combined with defects in SWR-C/Htz1. a Genome instability was measured using three different GCR assays in which the counter-selectable genes CAN1 and URA3 were inserted as a single cassette in haploid strains at different positions in the non-essential terminal region of the left arm of chromosome V50. Selection against CAN1 and URA3 using the drugs canavanine (Can) and 5-fluoroorotic acid (5FOA), respectively, selects for GCRs with a breakpoint between the CAN1-URA3 cassette and the most telomeric essential gene on the left arm of chromosome V (PCM1); the DNA sequences in this breakpoint region influence the types of GCRs that are formed. In the “unique sequence” GCR (uGCR) assay, the breakpoint region contains only single-copy sequences. The “short repeated sequence” GCR (sGCR) assay contains single-copy sequences and the can1::PLEU2-NAT locus, which introduced two short homologies that mediate GCRs by HR: SUP53, which is a 114-bp gene encoding leucine tRNA, and ~100 bp of YCLWdelta5 sequence, which has homology to the long-terminal repeats of Ty1 and Ty2 retrotransposons. The breakpoint region in the “segmental duplication” GCR (dGCR) assay contains the ~4 kb DSF1-HXT13 segmental duplication with divergent homology to regions of chromosomes IV, X, and XIV in addition to SUP53 and the YCLWdelta5 fragment. b. The uGCR, sGCR, and dGCR assays preferentially select for different kinds of GCRs in wild-type strains49, 50, 77, 78. c. Patch test for the formation of GCRs in the dGCR assay in SWR-C/Htz1 single mutants and corresponding double mutants containing the mrc1Δ or mrc1-aq mutation. Increased numbers of papillae correspond to increased GCR rates