Fig. 6.
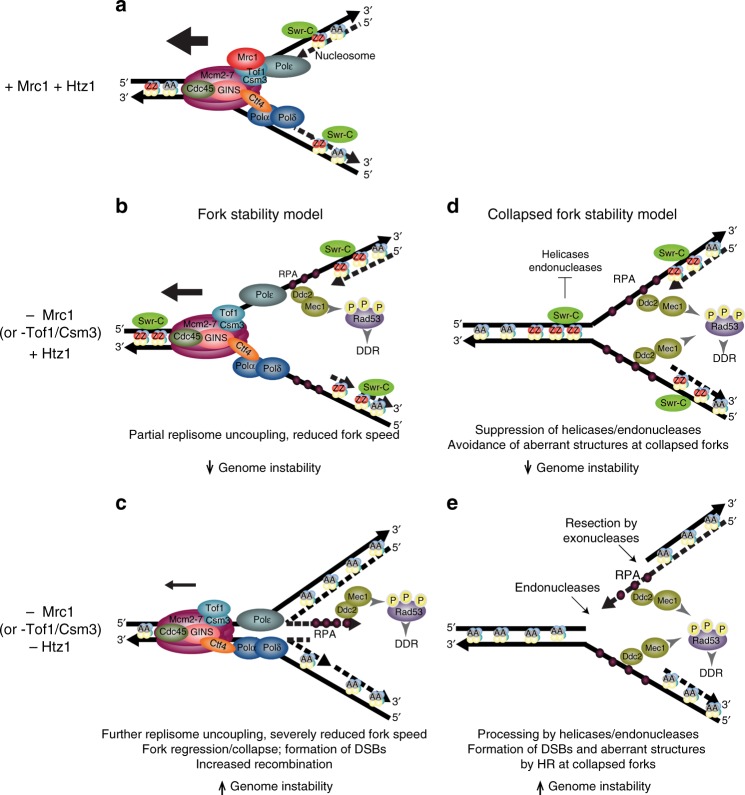
Hypotheses for the role of Htz1 in preventing genome instability. a Schematic of a normal replication fork showing key components including the Cdc45-Mcm2–7-GINS helicase complex, the leading (Polε) and lagging strand (Polα and Polδ) DNA polymerases, Ctf4, which couples the helicase and Polα, and Mrc1, which couples the helicase and Polε and interacts with Tof1-Csm3. Other replisome components are omitted for clarity. Also shown are nucleosomes containing the canonical histone H2A (grey circles) or the histone variant H2A.Z/Htz1 (red circles), which is incorporated by the SWR-C. b (Fork Stability Model) In the absence of Mrc1, replication fork progression is slowed and replisome uncoupling can occur during replication stress. The DNA damage response (DDR) is constitutively induced. The presence of Htz1 in normal chromatin prevents further replisome uncoupling or fork regression and collapse, preventing genome instability. The absence of Tof1 or Csm3 leads to similar albeit weaker defects. c In the absence of Mrc1 and Htz1, replication fork progression is severely impeded. Although DDR signaling is not elevated relative to the loss of Mrc1 alone, abnormal replication intermediates are formed, which are processed into DSBs. HR repairs the DNA damage and is required for survival during replication stress. Repair of the DNA damage using non-allelic targets leads to elevated genome instability. d (Collapsed Fork Stability Model) In the absence of Mrc1, increased levels of collapsed forks are formed. Remaining single-stranded DNA regions induce checkpoint activation, but incorporation of Htz1 near the sites of damage suppresses Rad51 filament formation and other HR-mediated repair processes, allowing the collapsed fork to be repaired by approach of an oppositely oriented fork. e In the absence of Mrc1 and Htz1, the collapsed fork is subjected to processing by structure-specific helicases and endonucleases, resulting in DSBs and other substrates for intermolecular HR, which generate aberrant replication fork structures and GCRs