Figure 7.
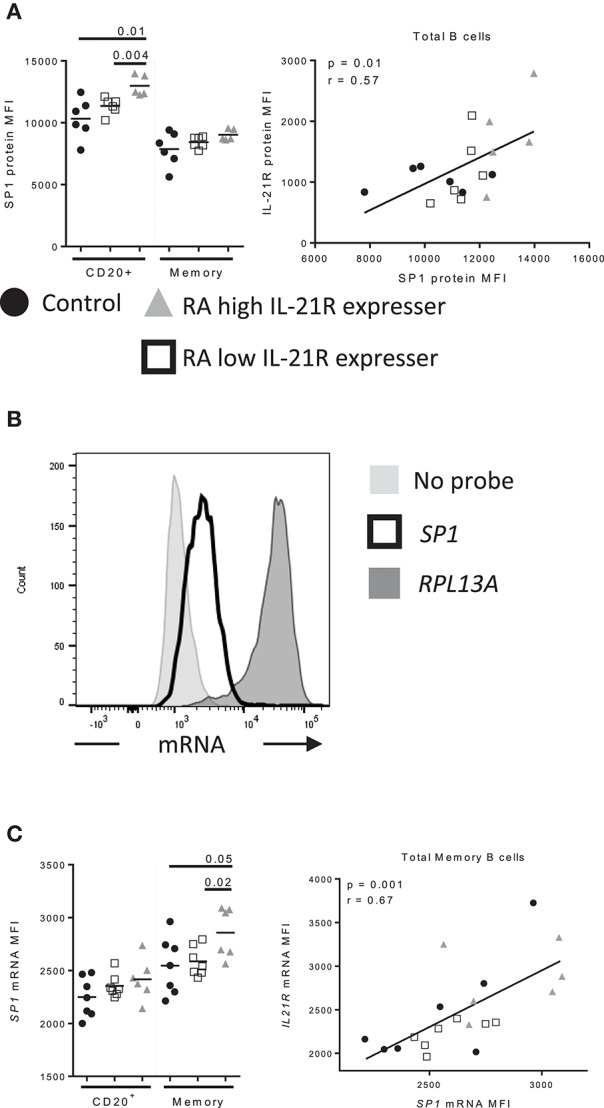
Increased SP1 expression correlates with increased IL-21R expression in memory B cells in RA subjects (A) SP1 protein levels were assessed by flow cytometry in control (n = 6, black circles), RA low IL-21R expressers (n = 6; open squares) and RA high IL-21R expressers (n = 5; gray triangles) in CD20+ and memory B cells (CD20+CD38−CD24+) (left). SP1 protein levels from left were correlated with IL-21R protein expression in total B cells in RA and control subjects (n = 17) (right). (B) Representative histogram of mRNA levels from a no probe negative control, SP1 and positive control probe, RPL13A. (C) (left) SP1 mRNA levels were determined in total memory B cells in controls (n = 7, black circles), RA low IL-21R expressers (n = 7; open squares) and RA high IL-21R expressers (n = 6; gray triangles). (right) SP1 mRNA levels from left were correlated with IL-21R protein expression in memory B cells in RA and control subjects combined (n = 20). Significance was determined using Mann Whitney U tests (to compare RA-IL-21high to controls and RA-IL-21low) and correlations were assessed with Pearson correlations.
