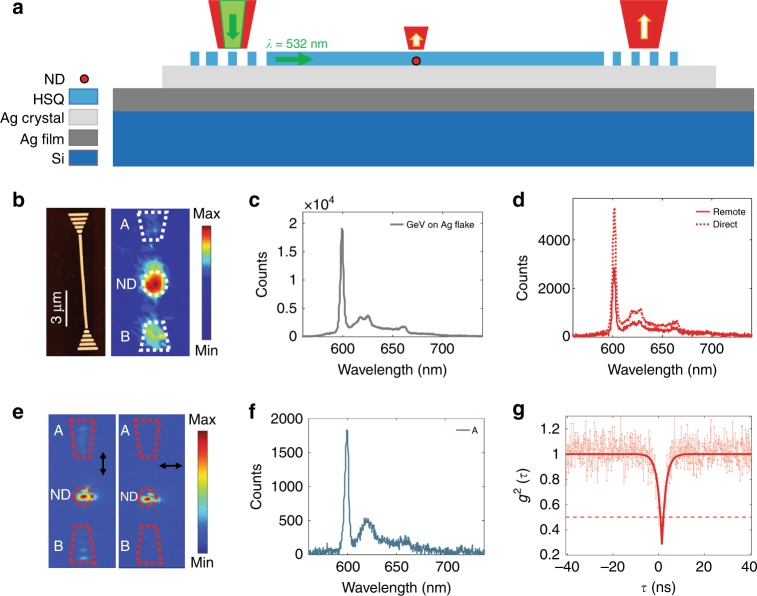
Fig. 5. On-chip remote excitation of a single GeV nanodiamond.
a Schematic of a sample layout for on-chip remote excitation of a GeV nanodiamond embedded in the plasmonic structure. b AFM image of the fabricated waveguide (b, left) and galvanometric mirror scan image showing the remote excitation of the embedded GeV where the pump laser light is illuminated at end B (b, right). Higher emission at end B is caused by the background fluorescence from the grating coupler exposed to the strong pump light. c, d Spectra taken from the uncoupled GeV, i.e. the nanodiamond on the Ag plate (c) and from coupled GeV when excited remotely (d, solid line) and in the case of direct excitation (d, dotted line). e CCD images for the coupled system when excited directly and with a linear polarizer placed in the detection path are presented for two orthogonal polarizations, parallel (left) and perpendicular (right) to the waveguide axis. f Spectrum taken from the outcoupled light through grating end A in the case of remote excitation. The integration time on the spectra data is 300 s, and the excitation powers are 2 μW (c, d) and 5 μW (f). g Second order correlation function of the GeV emitter confirming a single photon emission