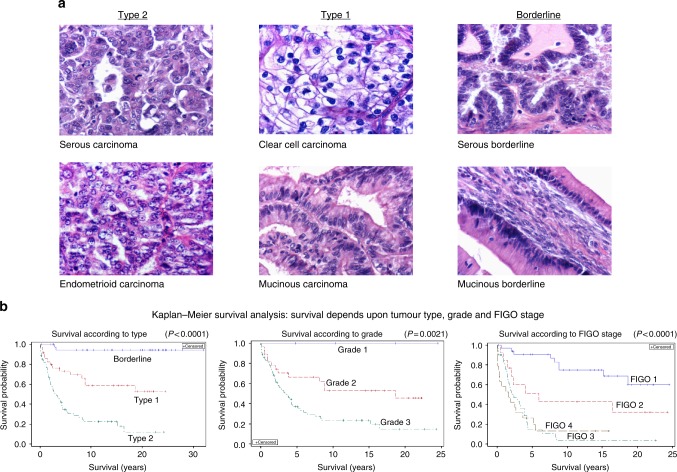
Fig. 1.
a Histopathology of ovarian tumour subtypes (×400): Serous carcinoma. Most frequent ovarian carcinoma. It can be either high grade (type 2) or low grade (type 1). Endometrioid carcinoma. Can be either high grade (type 2) with few glandular spaces, or low grade (type 1) with glandular spaces suggestive of endometrial glands. Clear cell carcinoma. This type 1 carcinoma contains cells with clear cytoplasm. Mucinous carcinoma. Mucin containing cells in this type 1 carcinoma are arranged in a disorderly fashion. Serous borderline. Tumour cells contain eosinophilic or amphophilic cytoplasm and are columnar or cuboidal in shape and line a cystic cavity in an orderly fashion. Mucinous borderline. Tumour cells are orderly in their arrangement, line a cystic cavity, and contain much mucin, which maybe either eosinophilic or basophilic. b Kaplan–Meier survival analysis demonstrates that patient survival depends upon ovarian tumour type, grade, and FIGO stage (p < 0.0001)