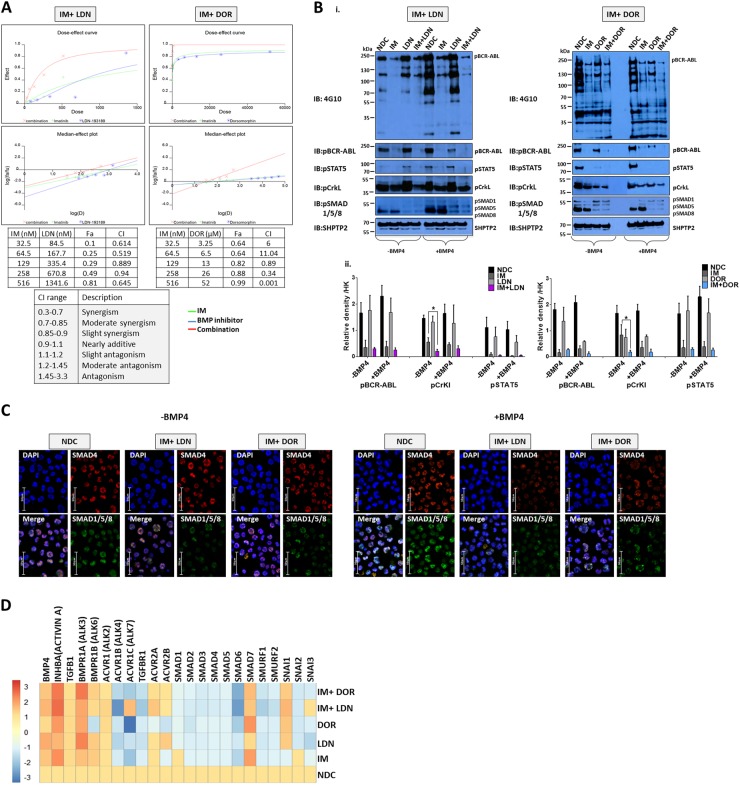
Fig. 2. IM and BMP pathway inhibitors synergistically target the K562 CML cell line.
a Synergy studies of the BMP pathway inhibitors, LDN-193189 (LDN) and Dorsomorphin (DOR) with imatinib mesylate (IM) were performed using CalcuSyn to quantify additive, synergistic and inhibitory effects. Tables present the fraction of cells affected (Fa) and combination index (CI) values at different combination concentrations. The bottom table describes the correlation between CI range and synergism. As shown, both LDN and DOR, in combination with IM, synergistically induce cell death in K562 cells. b Protein analysis of K562 cells treated with IM, BMP inhibitors and the combination (IM = 500 nM, LDN = 500 nM, DOR = 2.5 μM, n = 3) compared to no-drug control (NDC) using western blot hybridisation following drug treatment in the presence and absence of BMP4 stimulation. i IM and LDN combination immunoblots at 4 h (left panel) and IM and DOR combination immunoblots at 4 h (right panel). K562 cells were stimulated with 20 ng/mL BMP4 for 30 min; this was followed by drug treatment. SHP2 was used as the housekeeping protein. ii Densitometry analysis of western blots was performed using image J software. Analysis was normalised relative to the housekeeping protein expression. Both BMP inhibitors synergistically inhibit pCrKl significantly in the absence of BMP4 stimulation. Data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation and were compared using the unpaired Student’s t-test, *p < 0.05; n = 4. c Protein analysis using immunofluorescence in K562 cells treated with IM, BMP inhibitors and the combination of both (n = 3) at 24 h ± BMP4 stimulation. Panels of four pictures for each treatment include a single staining for SMAD1/5/8 in green, SMAD4 in red, the combination of both as the merge and no antibody in DAPI blue. d CD34+ primary CP-CML samples (n = 4) were treated with IM, BMP inhibitors and the combination of both (IM = 1 µM, LDN = 1 µM, DOR = 2.5 μM). Expression of BMP pathway genes was assessed at 72 h using the Fluidigm Biomark system; data were normalised to untreated cells