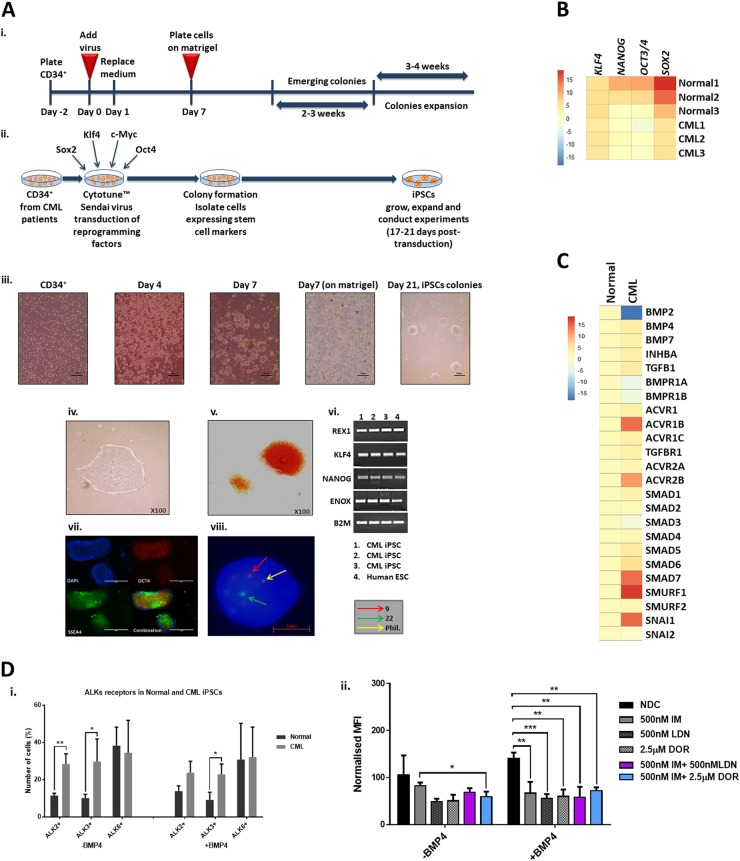
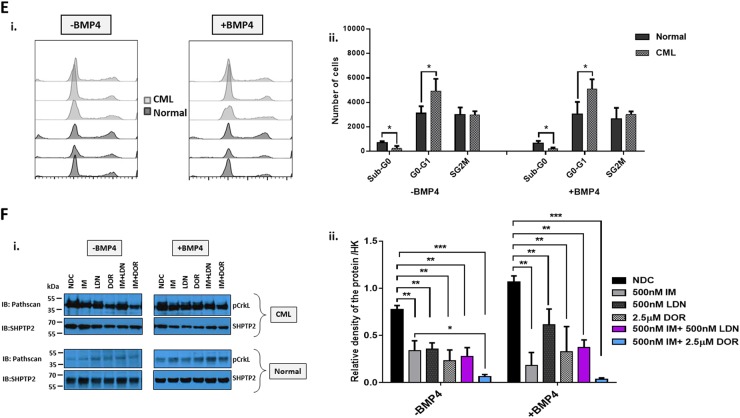
Fig. 6. Deregulation of the BMP pathway in CML-iPSC.
a Schematic representation of generating iPSCs from treatment naive CP-CML and normal samples using Sendai virus transduction of the reprogramming genes. i Experiment timeline for reprogramming CD34+ cells. ii A schematic representation of Sendai virus reprogramming of CD34+ cells from CP-CML patients. iii The morphology of cells during reprogramming period from single cells in suspension to iPSC colonies attached to matrigel coated plates. iv An iPSC colony with defined edges and a compact core. iPSCs were regularly passaged and colonies with highest pluripotency quality were plucked to help maintain this morphology. v Alkaline phosphatase (APh) staining. vi The expression level of REX1, KLF4 and NANOG were assessed by PCR in all iPSCs. vii Immunofluorescence staining with TRA1-60, SOX2, OCT4 and SSEA4 was used to confirm pluripotency at protein level in iPSCs. viii Fluorescent in situ hybridisation (FISH) confirming the presence of BCR-ABL translocation in CML-iPSC colonies. b qRT-PCR confirming the expression of important pluripoptency genes in the three normal and three CML-iPSC samples. c The expression level of BMP pathway components analysed using qRT-PCR in CML-iPSCs. Data were normalised relative to normal-iPCSs. d-i Analysis of BMPRIs (ALK2, 3 and 6) in normal and CML-iPSCs using flow cytometry. To stimulate BMP pathway, cells were treated with 20 ng/mL BMP4 for 24 h prior to experiment. CML-iPSCs express significantly higher levels of ALKs 2 and 3 in the presence and absence of BMP4 stimulation compared to normal samples. ii FACS analysis of ALK2 expression in CML and normal iPSCs following drug treatment. Results are expressed relative to NDC. e Cell cycle analysis of normal and CML-iPSCs in the presence and absence of BMP4 stimulation. f-i Protein analysis of pCrKL in normal and CML-iPSCs treated with IM, BMP inhibitors and the combination of both using immunoblotting ± BMP4 stimulation at 4 h. SHPTP2 was used as a control. ii Statistical analysis of immunoblots shows that dual inhibition using IM and DOR has a synergistic effect on reducing pCrKl levels in CML-iPSCs. Data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation and were compared using Anova and the unpaired Student t-test, ***p < 0.001–0.0001, **p < 0.01–0.001, *p < 0.05–0.01, n = 3