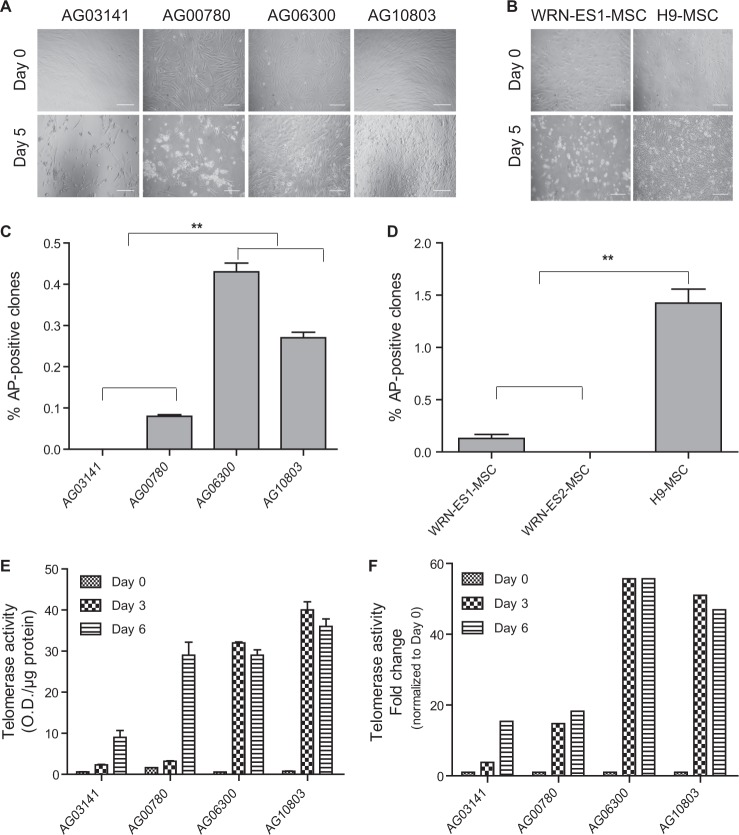
Fig. 1. The Yamanaka factors fail to stimulate iPSC generation from one specific WS fibroblast line.
a Representative images of WS (AG03141, AG00780, AG06300) and WT (AG10803) fibroblasts before Sendai virus infection and on Day 5 post-infection. Bar = 100 μm. b Representative images of WRN knockout (WRN-ES1) and WT (H9) human embryonic stem cells-derived MSCs before Sendai virus infection and on Day 5 post-infection. Bar = 100 μm. c The efficiency of iPSC generation from WS and WT fibroblasts. Values represent the mean percentage of alkaline phosphatase (AP)-positive clones among the number of plated cells. **P < 0.001. d The efficiency of iPSC generation from WRN-ES1-, WRN-ES2-, and H9-derived MSCs. Values represent the mean percentage of alkaline phosphatase (AP)-positive clones among the number of plated cells. **P < 0.001. e Telomerase activity of WS and WT groups at reprogramming Day 0, 3, and 6. f Fold change of telomerase activity at different reprogramming time points (Day 3, Day 6) normalized to that of Day 0 in WS and WT groups. WS Werner syndrome, WT Wild-type, WRN-ES WRN knockout human embryonic stem cells, H9 WT human embryonic stem cells