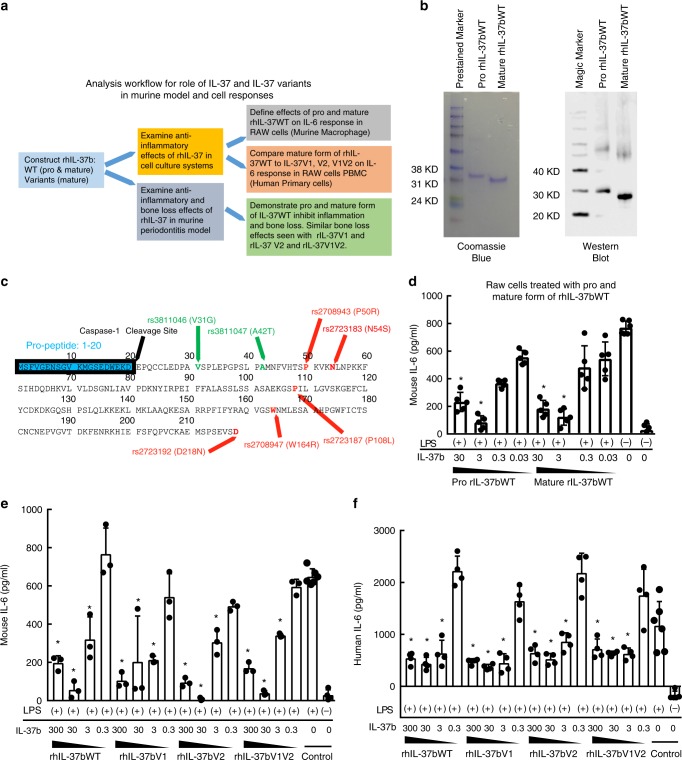
Fig. 5.
rhIL-37bWT and variants suppress RAW and PBMC response to LPS in vitro. a The analysis workflow for role of IL-37 and IL-37 variants in murine and human cell responses and murine periodontitis model. b The protein sketch of pro-IL-37b including cleavage site (amino acid 20) and variant sites (green: V1, red: V2). c Pro and mature rhIL-37b extracted from E. coli were detected on a 12% SDS–PAGE and analyzed by Coomassie blue and western blot using anti-IL-37 antibody. d IL-6 production in supernatant of RAW cells treated with gradient concentrations of pro and mature rhIL-37b following LPS (50 ng/ml) stimulation. Data show the mean±SD. *p < 0.05 (One-way ANOVA and Dunnett’s multiple comparisons tests, compare the mean of each group with the mean of LPS alone stimulation group). (+) or (−) indicate the cells with or without LPS stimulation. Results are representative of three independent experiments. e IL-6 production in supernatant of RAW cells treated with different concentrations of mature form of WT, V1, V2, and V1V2 rHIL-37b following LPS (50 ng/ml) stimulation. Data show the mean ± SD. *p < 0.05 (One-way ANOVA and Dunnett’s multiple comparisons tests, compare the mean of each group with the mean of LPS alone stimulation group). Results are representative of three independent experiments. f IL-6 production in supernatant of human PBMC cells treated with different concentrations of mature form of WT, V1, V2, and V1V2 rHIL-37b following LPS (50 ng/ml) stimulation. Data show the mean ± SD. *p < 0.05 (One-way ANOVA and Dunnett’s multiple comparisons tests, compare the mean of each group with the mean of LPS alone stimulation group). Results are representative of three independent experiments