Figure 6.
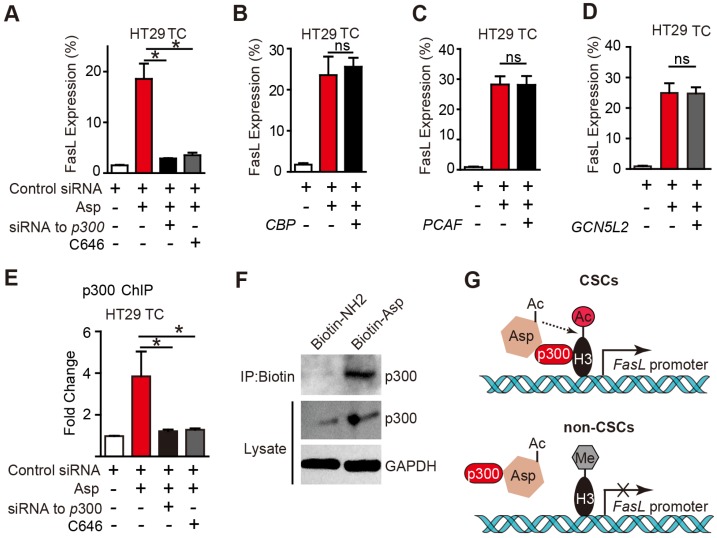
p300 is required for aspirin-induced acetylation of histone H3. (A-D) FCM assay of FasL expression in HT29 TCs treated with 5 mM Asp in the presence of siRNA against p300 or its inhibitor C646 (10 μM) (A), or siRNAs against CBP (B), PCAF (C), or GCN5L2 (D) (mean ± SEM, n=3). *, p<0.01, one-way ANOVA. (E) In vitro ChIP assay with antibodies against p300 followed by qPCR to detect fragments on the promoter of the FasL gene in HT29 TCs treated with 5 mM Asp, siRNA against p300, or C646 (mean ± SEM, n=3, normalized to the expression level of 10% input). *, p<0.01, one-way ANOVA. (F) In vitro IP assay. After 48 h treatment with 5 mM Biotin-NH2 or Biotin-Asp, HT29 TC lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-Biotin antibodies and immunoblotted with antibodies against p300 or GAPDH. (G) Diagram summarizing the difference between aspirin-induced effects in CSCs (upper) and non-CSCs (lower). (See also Figure S6)