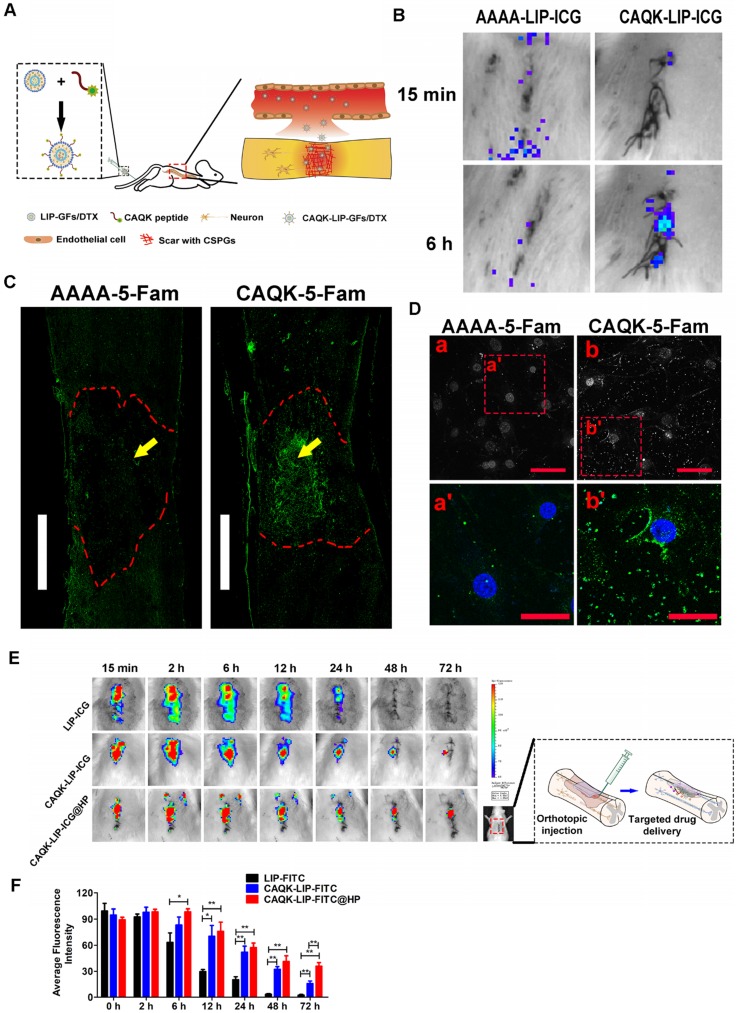
Figure 2.
CAQK-LIPs targeted drug delivery to the injury site and HP hydrogels improved drug retention. (A) Schematic diagram of the specific binding of CAQK peptide-modified liposomes to the injury site. (B) In vivo spectrum imaging system (IVIS) images of the spinal cord injected with indocyanine green (ICG)-labelled peptides at 3 days after spinal cord injury (SCI). (C) Fluorescence spinal cord images of rats injected with 5-carboxyfluorescein (5-FAM)-labelled peptides at 3 days after SCI. Scale bar = 1000 µm. (D) Fluorescence of the active astrocytes after treating with 5-FAM-labelled peptides for 4 h. (E) In vivo spinal cord retention and penetration of the different LIP-ICG complexes measured using IVIS. (F) Quantitative analysis of (E). Scale bar = 50 µm. N= 3, *P < 0.05, **P< 0.01.