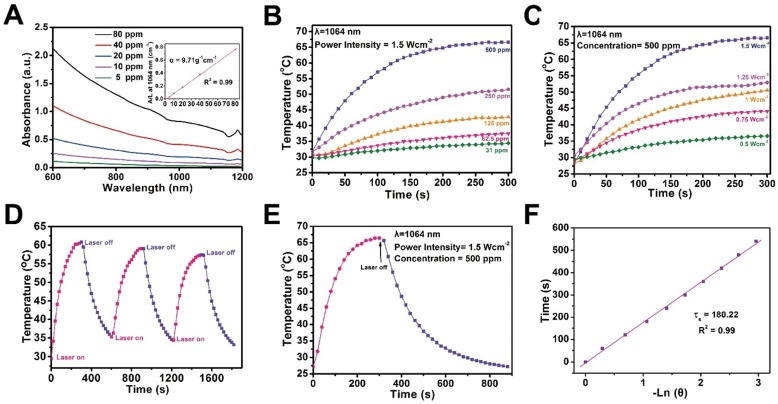
Figure 4.
In vitro photothermal conversion assessment of CTAC@Nb2C-MSN. (A) UV-vis spectra of CTAC@Nb2C-MSN at different concentrations (5, 10, 20, 40 and 80 μg/mL) in aqueous solution. Inset: mass extinction coefficient of CTAC@Nb2C-MSN at λ = 1064 nm. Normalized absorption intensity at 1064 nm divided by length of the cell (A/L). (B) Temperature changes of CTAC@Nb2C-MSN aqueous solution with NIR-II laser (1064 nm, power density: 1.5 W/cm2) irradiation at elevated concentrations (31, 61.5, 125, 250 and 500 μg/mL). (C) Photothermal heating curves of CTAC@Nb2C-MSN dispersed in aqueous solution irradiated by different power intensities (0.5, 0.75, 1.0, 1.25 and 1.5 W/cm2) of NIR-II laser at the wavelength of 1064 nm. (D) Heating curve of CTAC@Nb2C-MSN dispersed in water for three laser on/off cycles irradiated by a 1064 nm laser at the power intensity of 1.5 W/cm2. (E) Photothermal performance of CTAC@Nb2C-MSN dispersed in aqueous solution under NIR irradiation; the laser was turned off when the temperature was stable. (F) Time constant for heat process transfer calculated from the cooling period.