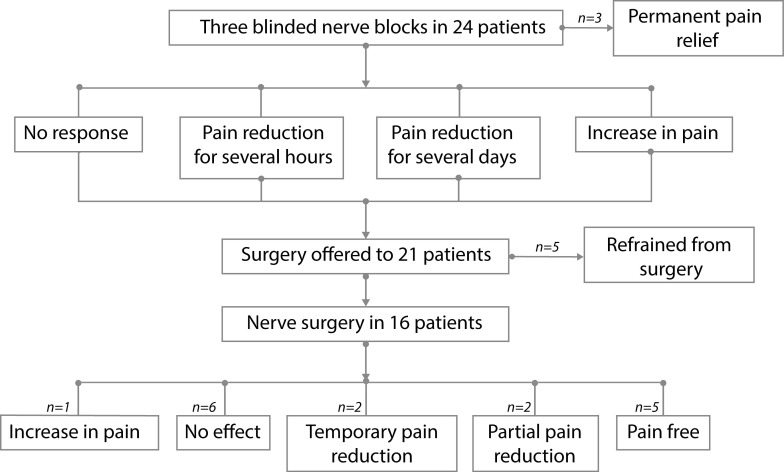
Fig 3. The effect on pain of three blinded nerve blocks in 24 patients with persistent postsurgical or nerve injury–induced probable neuropathic pain related to sensory nerves and results of nerve surgery.
Two weeks after each injection the response to the injection was documented. Two weeks after the third block, the content of all three provided injections was revealed to the patient and the effect of the injections was subsequently discussed. Regardless of the outcome of the three blocks, all patients were offered nerve surgery. A permanent positive effect on the pain following surgery was seen in 7/16 (44%) of the patients. No beneficial effect or an increase was reported by 9/16 (56%) of the patients. Five of the 16 patients (31%) were (as good as) pain free, and 2 (12%) had partial pain reduction. In 6/16 (38%) there was no effect of the surgery, whereas a temporary pain reduction was seen in 2 (12%) of the patients and an increase in 1 (6%).