Fig. 3. Action of M. gulosa venom peptides on vertebrate sensory neurons.
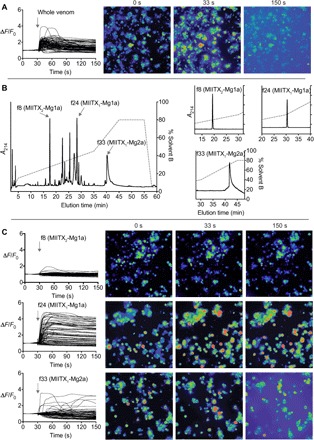
(A) Application of whole M. gulosa venom to DRG cells produced a rapid, non–cell-specific increase in [Ca2+]i followed by release of fluorescent dye into the medium. Each trace represents a single cell in the field of view. Snapshots shown of the recording are at 0 s (baseline), 33 s (3 s after addition of venom/fraction), and 150 s. (B) Three different peptides [fractions 8, 24, and 33 (f8, f24, and f33, respectively)] were purified from the whole venom using a single RP-HPLC step. Inset: Reanalysis of purified fractions by RP-HPLC. (C) Fraction 8 (MIITX2-Mg1a) had no effect on [Ca2+]i in sensory neurons, fraction 24 (MIITX1-Mg1a) caused an increase in [Ca2+]i in all sensory neurons, while fraction 33 (MIITX1-Mg2a) induced nonspecific permeabilization of cell membranes.
