Fig. 5. IKKβ phosphorylates RORγt Ser489, leading to RORγt binding to AhR.
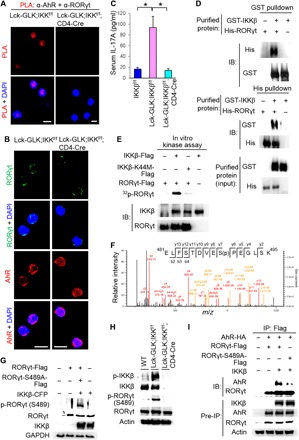
(A) Confocal microscopy analysis of PLAs for the interaction between endogenous AhR and RORγt in peripheral blood T cells from WT, Lck-GLK Tg, and Lck-GLK;IKKβf/f;CD4-Cre mice. (B) Confocal microscopy analysis of subcellular localization of AhR and RORγt in primary splenic T cells of WT, Lck-GLK Tg, and Lck-GLK;IKKβf/f;CD4-Cre mice. Original magnification, ×630; scale bars, 10 μm. (C) The serum levels of cytokines in 8-week-old mice were determined by ELISAs. IKKβf/f, n = 6; Lck-GLK, n = 6; Lck-GLK; IKKβf/f, n = 5. Means ± SEM are shown. *P < 0.05 (two-tailed Student’s t test). (D) Direct interaction between recombinant proteins of RORγt and IKKβ. GST or His pulldown assays of purified His-tagged RORγt and GST-tagged IKKβ proteins. (E) In vitro kinase assays of immunoprecipitated Flag-tagged RORγt and either IKKβ or IKKβ kinase-dead (K44M) mutant proteins from individual HEK293T transfectants. (F) Tandem MS (MS/MS) fragmentation spectra of the tryptic peptides of RORγt contain the phosphorylation of Ser489. m/z, mass/charge ratio. (G) Antibody specificity of anti–phospho-RORγt (Ser489) was demonstrated by immunoblotting using HEK293T cells cotransfected with CFP-tagged IKKβ plus either Flag-tagged RORγt WT or RORγt-S489A mutant. (H) Immunoblotting analyses of p-RORγt (Ser489), RORγt, p-IKKβ (Ser180/181), and IKKβ in primary splenic T cells of WT, Lck-GLK Tg, and Lck-GLK;IKKβf/f; CD4-Cre mice. (I) Coimmunoprecipitation experiments of HA-tagged AhR and either Flag-tagged RORγt WT or RORγt-S489A mutant using lysates of HEK293T cells cotransfected with vector or IKKβ-CFP plasmid. WT, wild-type littermate controls; Lck-GLK, T cell–specific GLK Tg mice; Lck-GLK;IKKβf/f;CD4-Cre, T cell–specific GLK Tg mice bred with IKKβ cKO mice. For PLA, each red dot represents a direct interaction. T cell nucleus was stained with DAPI (blue). Data shown (A, B, D, E, and G to I) are representative of three independent experiments.
