Figure 1.
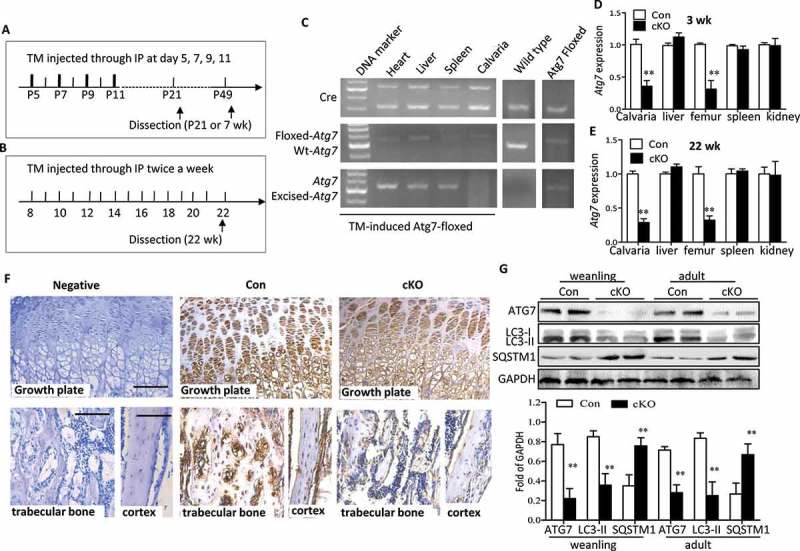
Ablation of Atg7 gene in TM-Atg7−/- (cKO) mice at P21- and 22-wks-old. (a and b) Scheme of the experimental design: In weanling mice, TM (0.2 mg/mouse) was injected intraperitoneally at day 5, 7, 9, 11 until dissection at P21. For adult stages, TM (50 mg/kg) was injected intraperitoneally twice a week from 8 wk until dissection at 22 wk. Both control mice (Cre−Atg7flox/flox) and cKO mice (Cre+Atg7flox/flox) received TM. (C) At 22 wk, PCR analyses of gDNA extracted from different tissues with primer sets for the Cre transgene, floxed-Atg7 allele, and sequences after gene excision (Atg7). (d and e) Quantitative RT-PCR shows reduced expression of Atg7 in femur and calvaria from P21 and 22-wk mice (n = 5 to 7/group) after TM administration. Results were presented as gene expression levels in all groups normalized to controls. (f) ATG7 protein in tibia from weanling mice assessed by immunohistochemistry. Scale bars: 100 μm. (g) Protein extracted from the calvaria of P21- and 22-wk-old mice was immunoblotted with antibodies directed to ATG7, LC3-I/-II and SQSTM1 (n = 3 or 4/group). Representative immunoblots and densitometric analysis are shown. *Statistically significant difference between Atg7 cKO and controls (mean ± SD, Student t test; **p < 0.01). Con: TM-Atg7flox/flox; cKO: TM-atg7−/-).
