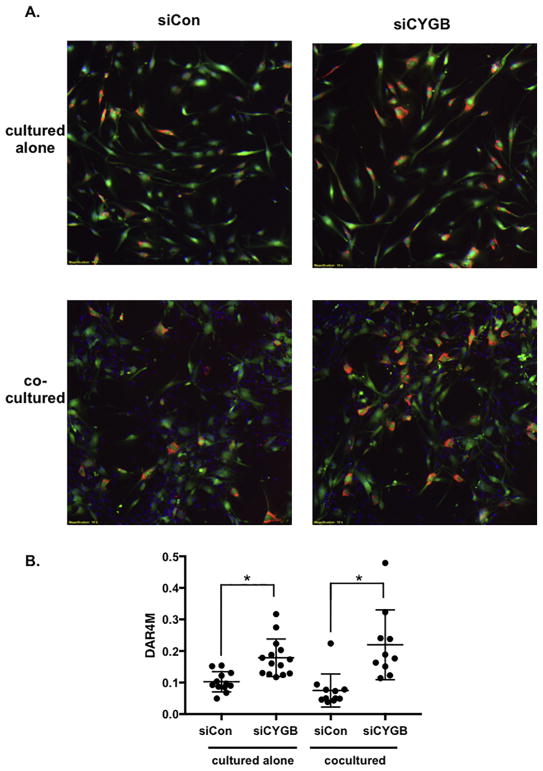
Figure 7. Nitric oxide is increased in cytoglobin-deficient smooth muscle cells.
(A) Images of cultured cells costained with a tracker dye (green) to visualize aortic smooth muscle cells, and DAR4M (red) to detect nitric oxide. DAPI (blue) was used to highlight nuclei and can be seen in the unlabeled endothelial cells in images from cocultured cells. Aortic smooth muscle cells were transfected with control siRNA (siCon) or siRNA to target cytoglobin (siCYGB), then labeled with tracker dye prior to coculture. (B) Graph of DAR4M staining (nitric oxide quantification) of captured images. DAR4M (red pixels) normalized to SMC (green pixels). Data points represent individual images taken from three separate experiments. *P < 0.05.