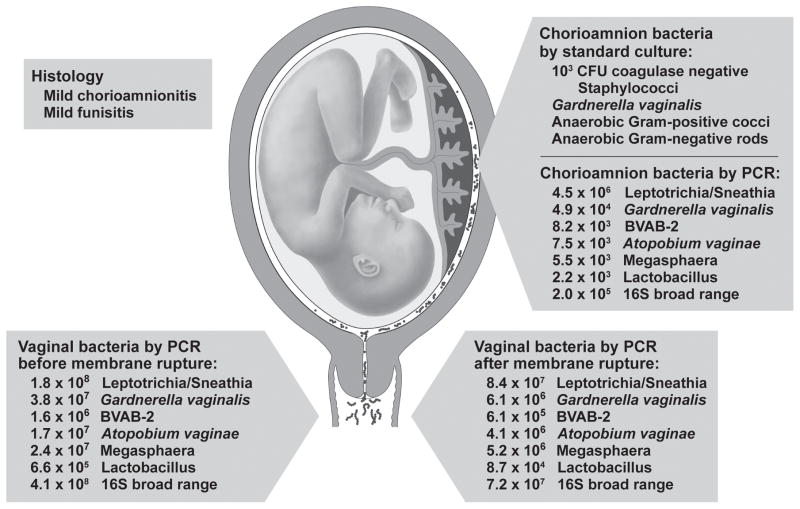
Figure 1.
Placental Cultures, Histopathology and Species-Specific qPCR for a Woman in Labor. Standard cultures and species-specific qPCR reveal the complexity of a polymicrobial infection in a woman in labor (case 19, Table 1). In this case, multiple BV-associated bacteria were detected in both the chorioamnion and vagina in the setting of mild chorioamnionitis and funisitis before and after rupture of the chorioamniotic membranes. The combination of parallel detection of the same bacterial species in the chorioamnion and vagina with a quantitative gradient (higher vaginal levels, lower chorioamnion levels) suggests microbial trafficking of these bacteria from the vagina and into the placenta. Copy numbers in the figure are per swab.