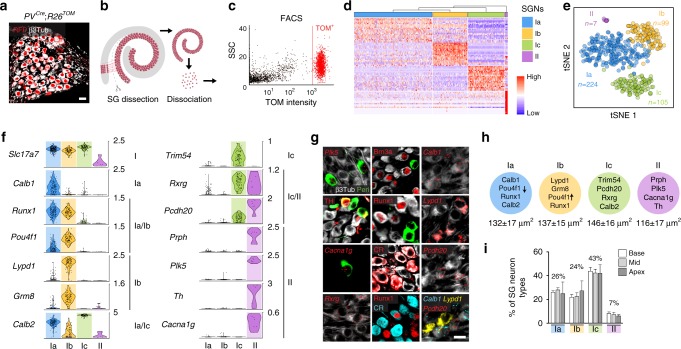
Fig. 1.
Identification and validation of four neuronal types in adult SG. a Genetic tracing of SG neurons (β3Tub+/RFP+) on P21 sections from PVcre;R26TOM mice. b Sketch depicting dissection of SG from the organ of Corti and their dissociation. c Fluorescence-side scatter plot of dissociated single cells showing isolation of Tom+ SG neurons through FAC sorting. d Heat map showing single-cell expression of the top 20 differentially expressed genes in the four types of SG neurons, from combined data of P17, P21, and P33 neurons (SGNs, SG neurons). Dendritic tree shows the similarity between neuronal types. e tSNE plot showing four distinct types of SG neurons. f Violin plots showing the expression of marker genes in log-transformed scale among the four different populations of SG neurons. g In vivo validation of the identified SG neuron types by immunohistochemical and fluorescent in situ hybridization using identified marker genes in P21 cochlea. Type II neurons were identified by peripherin (Peri), Plk5, TH, and Cacna1g specifically. Ia neurons were identified by Calb1, Pou4f1, Runx1, and calretinin (CR). Ib neurons were identified by Lypd1, Runx1, and Pou4f1 and Ic neurons, by Rxrg, Pcdh20, and CR expression. Note that co-localization on sections could never be observed for markers expressed in different populations of neurons in the scRNAseq data. h Schematic representation of neuronal types with their key markers and their average soma size (in µm2) at P21. i Proportion of SG neurons types along the tonotopic gradient (from base to apex) quantified by Runx1, Peri, and CR expression at P21 (n = 3 animals; Data are represented as mean ± SEM). Scale bars: 20 μm (a,g)