Fig. 5.
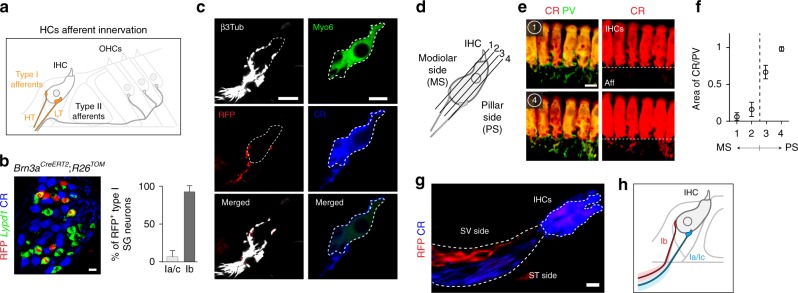
Innervation pattern of IHCs by type I neurons. a Sketch representing the afferent innervation of the mature organ of Corti, and illustrating the spatial segregation of the peripheral projections and synaptic contacts of high threshold (HT) and low threshold (LT) SG neuron fibers with IHCs. HT fibers innervate the modiolar side while LT fibers, the opposite, pillar side of IHCs. b Genetic labeling of Ib neurons using Brn3aCreERT2;R26TOM, injected with tamoxifen at P21 and analyzed on cross-section at P30. About 96% of RFP+ cells were Lypd1+ and were CR−, confirming their Ib identity (n = 3 animals). c In Brn3aCreERT2;R26TOM mice, RFP+ Ib fibers innervate the modiolar side, while CR+ Ia and Ic fibers, the pillar side of IHCs. In the merged panel for the CR (Ia/Ic fibers) and Myo6 (IHC) staining, the IHC is shadowed to better visualize the innervation. d Schematic of the position of sections shown in e and f. e Whole mount staining of P21 cochlea, using CR and PV immunostaining in WT mice. The images show the presence of CR+ fibers on the pillar side (PS, section #1) and their absence on the modiolar side (MS, section #4) of IHCs, while PV+ afferents are observed on either side (Aff: afferents). f Quantification of the distribution of CR+ afferent fibers at different section levels of the IHCs (from the modiolar side to the pillar side) by measuring the area of the CR+ fibers within the area of PV+ fibers at different levels of the IHC innervation, as shown in d and e (n = 4 animals). Note that no CR+ fibers were observed outside the PV+ fibers area. g In Brn3aCreERT2;R26TOM mice (see b), the peripheral projections of Ib (RFP+) and of Ia/Ic (CR+) neurons within the osseus lamina are segregated and occupy the scala vestibuli (SV) and scala tympani (ST) sides, respectively. h Schematic summary of the IHC innervation by type I afferents. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. Scale bars: 20 μm (b,c); 10 μm (e,g)