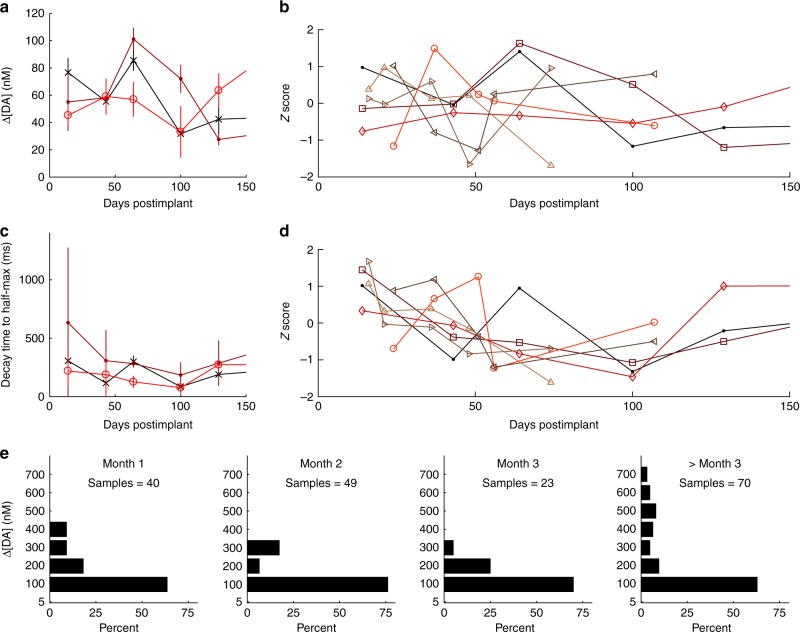
Fig. 3.
Chronically implanted µIPs provide reliable longitudinal measurement over a wide range of dopamine concentrations and over the course of months postimplant. a Measured dopamine (DA) over time from three different probes, c121 (×), c122 (•), and c123 (○), in a single rat for a fixed stimulation parameter. b Recorded dopamine concentrations across time normalized to show fluctuations in measured dopamine release for each of 7 probes, c121 (•), c122 (⎕), c123 (◊), c171 (○), c172 (⊲), c201 (⊳), and c202 (▵), implanted in three rats. Stimulation parameters were fixed for each rat across measurement sessions. c Measured decay time from maximum to half-maximum evoked dopamine for same probes and parameters as in a. d Normalized decay times for same parameters and probes as in b. e Binned recorded dopamine concentrations detected by all functional probes (eight probes in four rats) and for the fixed stimulation parameters as in b and d, plotted by month. Error bars represent 95% confidence intervals