Fig. 5.
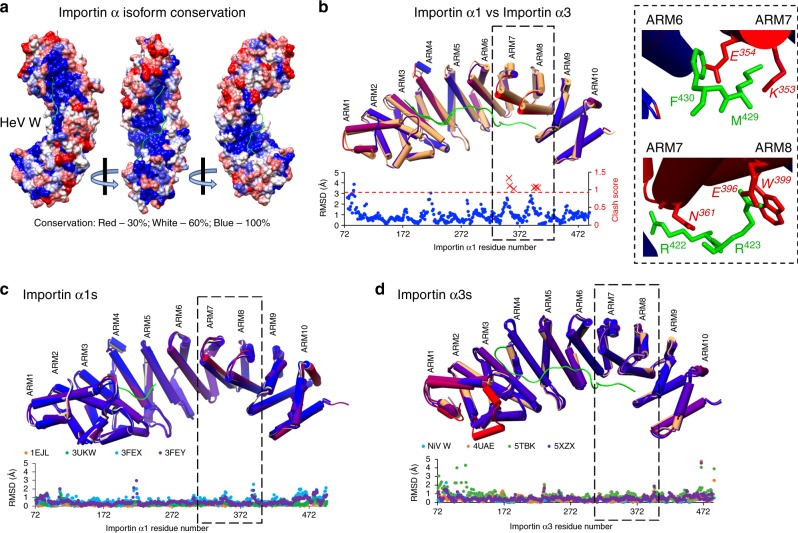
Structural basis for specificity of Henipavirus W binding to the importin α3. a Importin α3:HeV W structure coloured by conservation of amino acids across all importin α isoforms highlights a 100% conservation in the binding interface. The HeV W NLS backbone (coloured green) is shown in complex with importin α3, with sequence colour rendering red at 30%, white 60%, and blue 100% sequence identity. Figure created in UCSF Chimera using importin α alignments from Clustal Omega. b To identify structural differences, the structures of importin α1:HeV W and importin α3:HeV W were superimposed in UCSF Chimera using MatchEnsemble, and r.m.s.d. plots generated using MatchAlign, and MatchAssess functions. α-helices shown as cylinders; importin α3 coloured orange throughout, and colour conservation rendering for importin α1 set for blue, < 2.5 Å variance, and red for variances > 2.5 Å. Molprobity was used to analyse clash data of importin α3:HeV W NLS superimposed to importin α1, all clashes > 0.8 shown as red crosses. Differences in clash score between importin α1 and α3 are localised to ARMs 7 and 8. Detailed view of clashes are presented in the right box, highlighting residues clashing with the W NLS owing to the difference in positioning of ARMs 7 and 8 in importin α1. All clashing residues are positioned on the α-helices of the ARMs. c Structural comparisons of importin α1 bound to a range of cargo was examined by superimposing the α1:HeV W NLS structure determined in this study (reference molecule, coloured yellow), with importin α1 bound to a monopartite SV40T NLS12 (1EJL), bipartite Bimax NLS59,60 (3UKW), and two domain bound structures of CAP8061 (3FEX, 3FEY) coloured according to r.m.s.d as described in b. Positioning of the α-helices in ARMs 7 and 8 are relatively static across all structures. d Structural comparisons of importin α3 bound to a range of cargo was examined by superimposing the α3:HeV W NLS structure determined in this study (reference molecule coloured orange) with the monopartite RanBP362 (5ZXZ), the NiV W (this study), and domains of PB219 (4UAE) and RCC115 (5TBK) coloured according to r.m.s.d as described in b. Positioning of α-helices in ARMs 7 and 8 are also relatively static across all structures