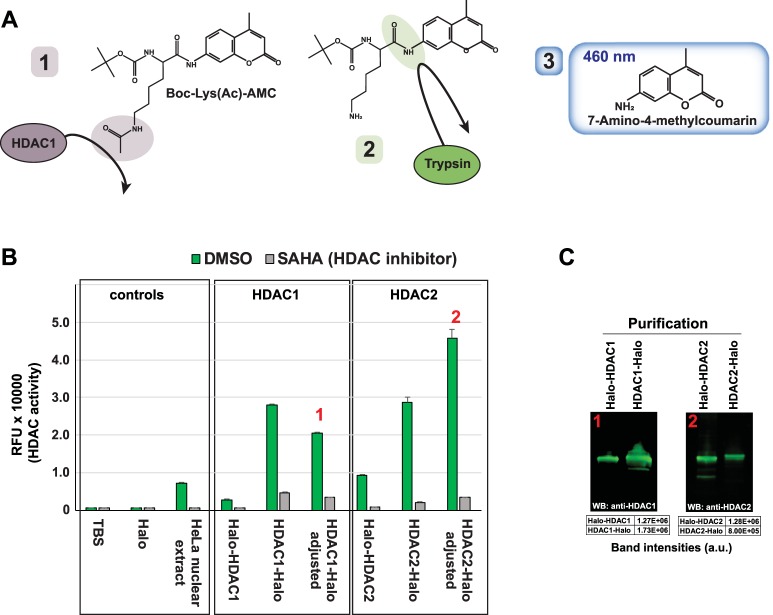
Figure 6.
HDAC1/2 deacetylase activity depends on the affinity tag location. (A) Substrate used to test HDAC activity. Boc-Lys(Ac)-AMC contains an acetylated lysine moiety that can be deacetylated by class I HDACs (1). Deacetylated substrate is recognized by trypsin (2), and subsequent trypsin digestion releases fluorescent 7-Amino-4-methylcouramin which emits light detectable at 460 nm (3). The structure of Boc-Lys(Ac)-AMC has been reproduced using data from National Center for Biotechnology Information PubChem Compound Database; CID = 9846360, https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/9846360 (accessed Apr. 17, 2018). (B) Activity of HDAC1/2 purified samples. HDAC activity assays were performed as described in Methods using equal volumes of eluate from the indicated purifications. Values are the mean of three technical replicates. Error bars represent standard deviation. Adjusted values account for differences in HDAC1/2 concentration between Halo-HDAC1 and HDAC1-Halo samples, or between Halo-HDAC2 and HDAC2-Halo samples determined by quantitative Western blotting using antibodies to either HDAC1 or HDAC2. (C) Relative amounts of HDAC1 or HDAC2 in Halo affinity purifications. Equal volumes of eluate from the indicated Halo affinity purifications were analysed by SDS PAGE and Western blotting. Purified HDAC1 or HDAC2 was detected using rabbit anti-HDAC1 or rabbit anti-HDAC2 primary antibody and IRDye® 800CW labeled goat anti-Rabbit secondary antibody. Fluorescently labeled secondary antibodies were detected using a Li-Cor Odyssey infrared imaging system. Band intensities were quantitated using Image Studio (version 2.1) software (Li-Cor). Full length images are presented in Supplementary Figure 5.