Figure 1.
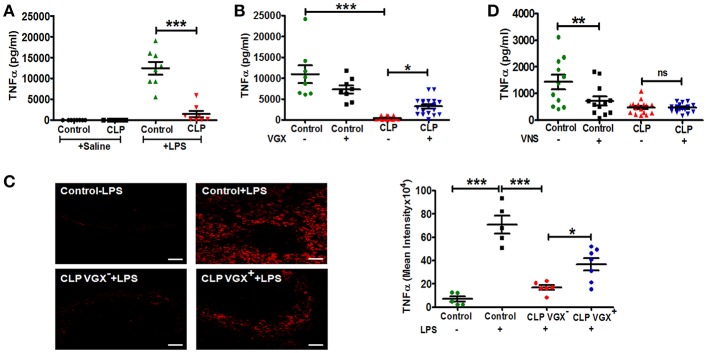
Vagotomy restores LPS-induced TNFα response in CLP-survivors. To assess the in vivo immune response of CLP-surviving mice to subsequent LPS challenge, BALB/c mice were subjected to control or CLP surgery, allowed to recover for 4 weeks, and then administered LPS (4 mg/kg) by intraperitoneal injection. Vagotomy (VGX) was performed 2 weeks post-CLP or control surgery. Blood and spleens were harvested 90 min after LPS administration. (A) Lower TNFα levels in serum of sepsis survivors in response to LPS challenge in vivo. (n = 8 mice/group). Results are the mean ± SEM from two independent experiments, Control + LPS vs. CLP + LPS ***p < 0.001 (Tukey's post hoc test). (B) Restoration of LPS-induced TNFα responses following bilateral subdiaphragmatic vagotomy in sepsis survivors. (n = 8–19 mice/group). Results are the mean ± SEM from three independent experiments, CLP VGX− vs. CLP VGX+ *p < 0.05 and Control VGX− vs. CLP VGX− ***p < 0.001 (Tukey's post hoc test). (C) Anatomical localization of splenic LPS-induced TNFα in sepsis survivors. (n = 5–7 mice/group). Results are the mean ± SEM from two independent experiments, CLP VGX− + LPS vs. CLP VGX+ + LPS *p < 0.05; Control without LPS vs. Control + LPS or Control + LPS vs. CLP VGX− + LPS ***p < 0.001 (Tukey's post hoc test). Magnification: (20X; scale bar = 50 μm). (D) Mice were subjected to with or without vagus nerve stimulation (VNS; 1 min) followed by LPS injection. Serum TNFα was measured by ELISA. (n = 11–16 mice/group). Results are the mean ± SEM from two independent experiments, Control VNS− vs. Control VNS+ **p < 0.01; CLP VNS− vs. CLP VNS+ ns = not significant (Tukey's post hoc test).