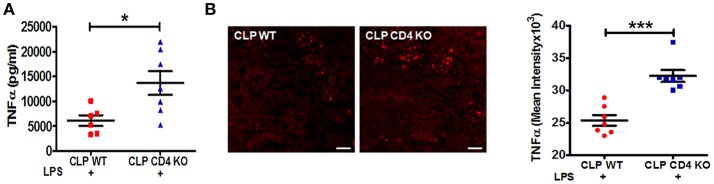
Figure 3.
CD4 T cell-deficiency restores LPS-induced TNFα responses in CLP-survivors. To identify the role of CD4+ T cells in mediating inflammatory reflex, C57BL6/J WT and CD4 knockout mice were subjected to CLP surgery, allowed to recover for 4 weeks, and then challenged with LPS by intraperitoneal injection (6 mg/kg). Blood and spleens were harvested 90 min after LPS administration. Serum TNFα was measured by ELISA. (A) Enhanced LPS-induced serum levels of TNFα in endotoxemic CD4 T cell-deficient CLP-surviving mice. Results represent the mean ± SEM of 6–7 mice per group from one of two independent experiments; CLP WT + LPS vs. CLP CD4 KO + LPS *p < 0.05. (Mann-Whitney U-test). (B) TNFα staining in spleen sections of CLP WT and CLP CD4 KO. Magnification (20X; scale bar = 50 μm). Images are representative of spleen sections from two independent experiments (n = 7). CLP WT + LPS vs. CLP CD4 KO + LPS ***p < 0.001. (Mann-Whitney U-test).