Figure 2.
Caveolin-1 Is Required for Immature Neurite Pruning and Leading Process Elongation
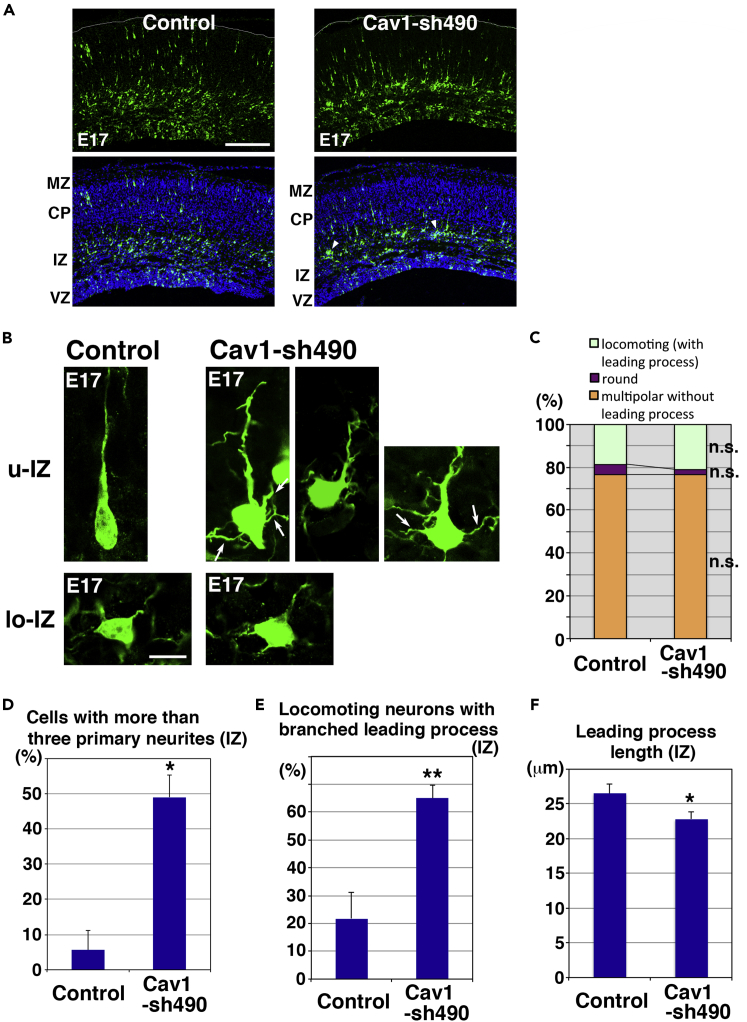
(A–F) Cerebral cortices at E17, electroporated with the indicated plasmids plus pCAG-EGFP at E14. (A) The lower panels show EGFP fluorescence (green) and nuclear staining with DAPI (blue). Arrowheads indicate small cell aggregates. (B) High-magnification images of the upper IZ (u-IZ) or lower IZ (lo-IZ) of the cerebral cortices. White arrows indicate abnormal primary neurites. (C) The ratio of cells with the indicated morphology in the IZ. Control and Cav1-sh490: n = 4 brains. No significant differences (n.s.) between control and Cav1-sh490-electroporated neurons were found by Mann-Whitney's U test and Student's t test (locomoting: p = 1 or 0.6148, round: p = 0.1489 or 0.1916, multipolar: p = 1 or 0.9484, respectively). (D and E) The ratio of locomoting neurons with more than three primary neurites (D) or branched leading processes (E) in the IZ. Control: n = 4 (52 cells) (D and E), Cav1-sh490: n = 5 (128 cells) (D) or 8 (171 cells) (E). Each score represents the mean of ratios ± SEM. Significance was determined by Mann-Whitney's U test [(D) p = 0.01431, (E) p = 0.006578) and Student's t test (D) p = 0.001542, (E) p = 0.0006317]. **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05. (F) Average leading process length of the locomoting neurons in the IZ. Control: n = 82 cells, Cav1-sh490: n = 85 cells. Each score represents the mean length ± SEM. Significance was determined by Welch's t test (p = 0.02834). *p < 0.05. See also Figures S6 and S7. Scale bars: 200 μm in (A) and 10 μm in (B).