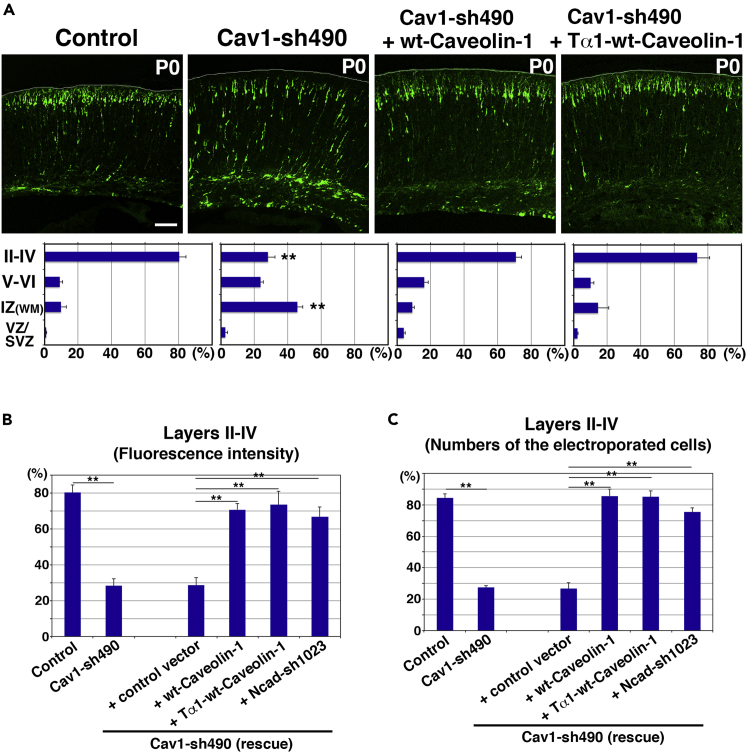
Figure 3.
Knockdown of Caveolin-1 Results in Neuronal Migration Defects
(A–C) Cerebral cortices at P0, electroporated with the indicated plasmids plus pCAG-EGFP at E14. The lower graphs in (A) show the estimation of cell migration, which was carried out by recording fluorescence intensities of EGFP in distinct regions of the cerebral cortices using Leica SP5 software. (B and C) The graphs show the ratio of the fluorescence intensities of EGFP (B) or the number of the electroporated cells (C) in the upper part of the cortical plate (future layers II–IV) to the whole cerebral cortices. Each bar represents the mean percentage of relative intensities ± SEM. Control: n = 6 brains, Cav1-sh490: n = 7 brains, Cav1-sh490 + CAG-wt-Caveolin-1: n = 8 brains, Cav1-sh490 + Tα1-wt-Caveolin-1: n = 6 brains. Significance compared with control was determined by Student's t test (A) or one-way ANOVA with post hoc Tukey-Kramer test (B and C). (A) Cav1-sh490 (layer II–IV) p = 0.000002286, Cav1-sh490 (IZ) p = 0.000007796. **p < 0.01. (B and C) ** p < the critical value at 1% (control versus Cav1-sh490, control versus Cav1-sh490 + control vector, Cav1-sh490 versus Cav1-sh490 + CAG-wt-caveolin-1, Cav1-sh490 versus Cav1-sh490 + Tα1-wt-caveolin-1, Cav1-sh490 versus Cav1-sh490 + Ncad-sh1023, Cav1-sh490 + control vector versus Cav1-sh490 + CAG-wt-caveolin-1, Cav1-sh490 + control vector versus Cav1-sh490 + Tα1-wt-caveolin-1, Cav1-sh490 + control vector versus Cav1-sh490 + Ncad-sh1023). II–IV, layers II–IV of the cortical plate; V–VI, layers V–VI of the cortical plate; IZ, intermediate zone; WM, white matter; SVZ/VZ, subventricular zone/ventricular zone. Scale bar: 100 μm in (A).