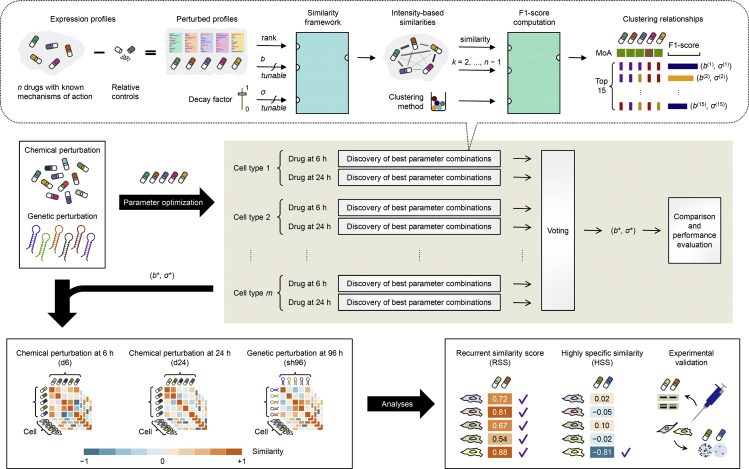
Figure 1.
Workflow of the Intensity-Based Similarity Framework
We accessed gene expression profiles corresponding to thousands of chemical and genetic perturbations across multiple cell lines from LINCS. To determine optimal parameters for the intensity-based similarity metric (query gene set size b and decay factor σ), we selected 74 chemical compounds corresponding to 10 mechanisms of action (MoAs) as the gold-standard clustering and then used majority voting to choose the most frequently occurring parameter combination that yielded the best clustering performance from their treatments at 6 or 24 hr across 10 cell types. For each metric paired with one clustering method, an optimal clustering was determined across a full range of number of clusters k with the best external cluster validity index F1 score. These intensity-based metrics and resultant clusterings were further compared with other state-of-the-art and commonly used metrics. We then used the optimal parameter set to compute pairwise intensity-based similarities for all available chemical and genetic perturbations and performed in-depth analyses to uncover perturbation pairs recurrently or exclusively similar among multiple cell types. Experimental validation of discoveries was performed for drugs showing immediate repurposing opportunities.