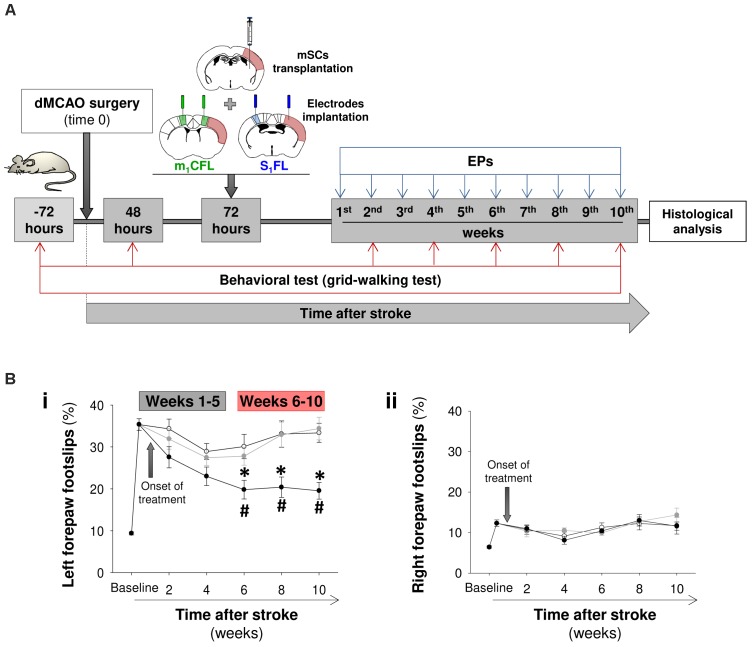
FIGURE 2.
Sensorimotor recovery in stroke mice treated with mSCs-silk fibroin hydrogels. (A) Schematic of the study performed to examine the temporal progression of sensorimotor function and evoked activity in FLs1 and cFLm1 regions. The stroke animals were divided into three groups and treated with a saline solution (PBS, white circles in B), mSCs (gray circles) or mSCs encapsulated in silk fibroin hydrogels (black circles). Sensorimotor coordination was evaluated with the grid-walking test before and after stroke at different post-treatment time points. The FLs1 and cFLm1 responses were obtained for several weeks after treatment. The schematics of coronal brain slices illustrate the site of cerebral injection (treatment) and the placement of electrodes in relation to the cortical damage (soft red) induced in this specific mouse stroke model. (B) Percentages of footslips examined with the grid-walking test for the left (panel i) and right forepaws (panel ii), respectively. The left forepaw was contralateral to the infarcted (right) hemisphere. Data are presented as the means ± the SEM from nine mice per group at the onset of the study (PBS, mSCs or mSCs-Silk fibroin). Asterisks denote significant differences in data at every time point analyzed between the mSCs-SF group and the other two treated groups. The hashed symbols show statistically significant differences compared with the baseline post-stroke pretreatment values (two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test; ∗p < 0.05).