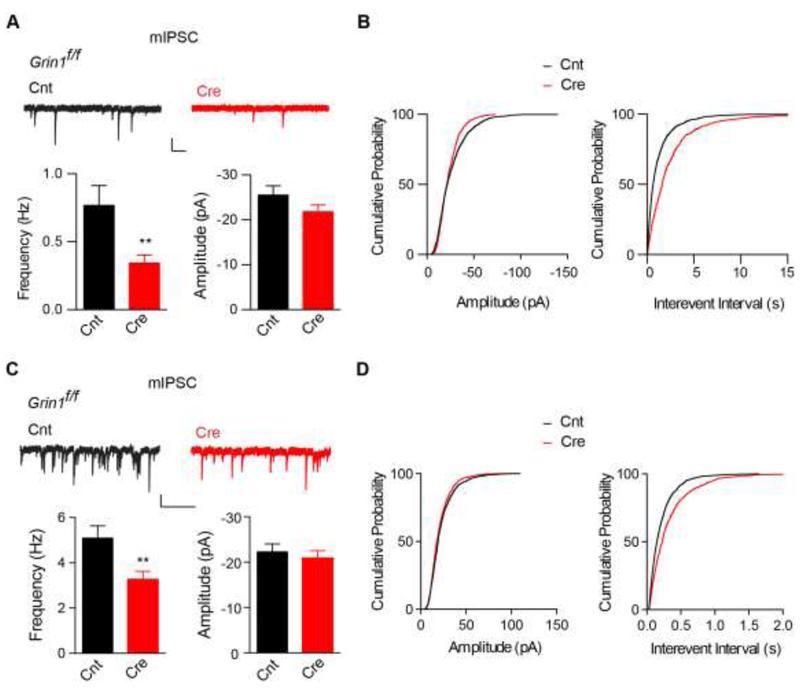
Figure 2. Loss of NMDARs in layer 2-3 pyramidal neurons in motor cortex decreases GABAergic synaptic transmission.
(A-B) Cre expression caused a strong reduction of mIPSC frequency in layer 2/3 pyramidal neurons from primary motor cortex from P9-10 Grin1f/f mice (Frequency: Cnt (0.77 ± 0.14 Hz, n = 10), Cre (0.34 ± 0.06 Hz, n = 11), p <0.01, t-test; Amplitude: Cnt (−25.5 ± 2.1 pA, n = 10), Cre (−21.8 ± 1.6 pA, n = 11), p = 0.67, t-test). Cumulative distributions were compared by the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test (p ≥ 0.05 for amplitude and p < 0.001 for interevent interval). Scale bar: 20 pA and 1s.
(C-D) Cre expression caused a significant reduction of mIPSC frequency in layer 2/3 pyramidal neurons from primary motor cortex from P17-18 Grin1f/f mice (Frequency: Cnt (5.1 ± 0.5 Hz, n = 9), Cre (3.3 ± 0.3 Hz, n = 8), p < 0.01, t-test; Amplitude: Cnt (−22.4 ±1.6 pA, n = 9), Cre (−21.0 ± 1.5 pA, n = 8), p = 0.74, t-test). Cumulative distributions were compared by the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test (p ≥ 0.05 for amplitude and p < 0.001 for interevent interval). Scale bar: 20 pA and 1s.