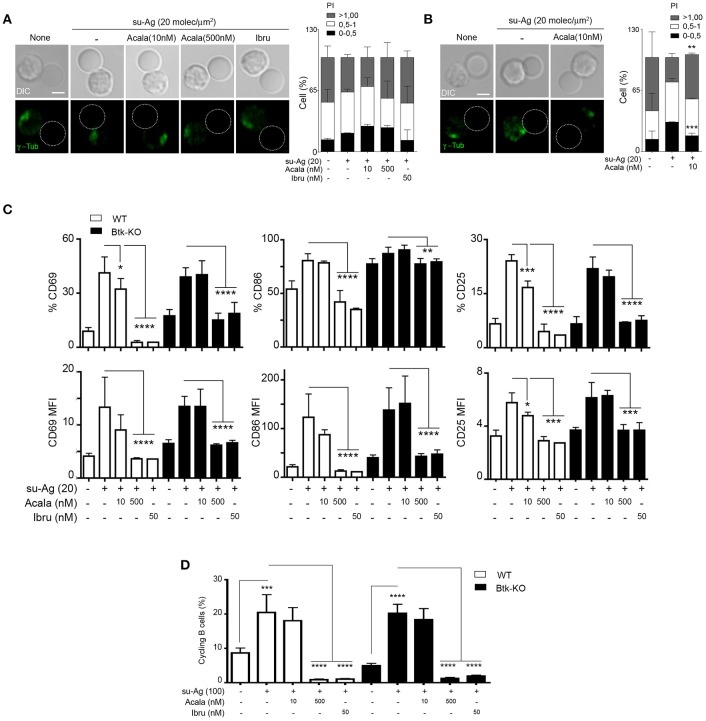
Figure 7.
Btk-KO B cells have impaired MTOC polarization, but no significant alterations in cell activation or proliferation. (A) DIC and fluorescence γ-tubulin (γ-tub; green) images are shown of representative Btk-KO B cell/pseudo-APC conjugates, fixed at 30 min, for each indicated condition. Dashed circle, pseudo-APC; right, frequency of B cells as in A, in the specified polarity index (PI) groups; data shown as mean ± SD of 60 B cells in each case. (B) As in (A) but for WT B cells in the specified conditions. (C) WT and Btk-KO B cells, untreated or treated with the indicated inhibitors, were co-cultured with pseudo-APC, unloaded (none) or su-Ag-loaded (20 molec/μm2; su-Ag-20) at 1:1 ratio, 20 h. Frequencies of B cells expressing CD69, CD25 or CD86 (top) and MFI values for these markers (bottom) in each condition and for each B cell type are shown. (D) Violet-labeled WT and Btk-KO B cells were co-cultured with pseudo-APC, unloaded (none) or su-Ag-loaded (100 molec/μm2, su-Ag-100, ratio 1:1), with IL-4, 72 h. Frequencies of cycling B cells (with diluted violet-tracer level) in each condition and for each B cell type are shown. Data in (A) are the merge of three experiments (n = 3), and in (B) of two experiments (n = 2); data in (C,D) are the mean ± SD of three experiments (n = 3). *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001 by Student's t-test with WT or Btk-KO in presence of su-Ag in each case. Bar 2 μm.