Figure 2.
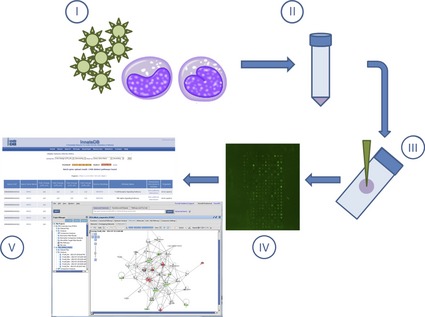
Overview of kinome peptide array experimental procedure. Host cells/tissues are infected in vitro or in vivo with pathogen of interest (I). Following infection for the desired time course, cells/tissues are isolated (pelleting by centrifugation or homogenized, respectively) followed by cell lysis (II). Cell debris is removed by high‐speed centrifugation, and supernatants are spotted on the kinome arrays (III). Arrays are incubated to allow for phosphotransfer from activated kinases in the supernatants to the specific peptide targets on the arrays followed by washing, staining, and imaging. (IV). Data are extracted from the spot intensities, and fold‐change differences in phosphorylation are derived using PIIKA followed by functional network analysis (ex. InnateDB or Ingenuity Pathway Analysis) (V).
