Figure 3. CIN activates cGAS-STING signaling.
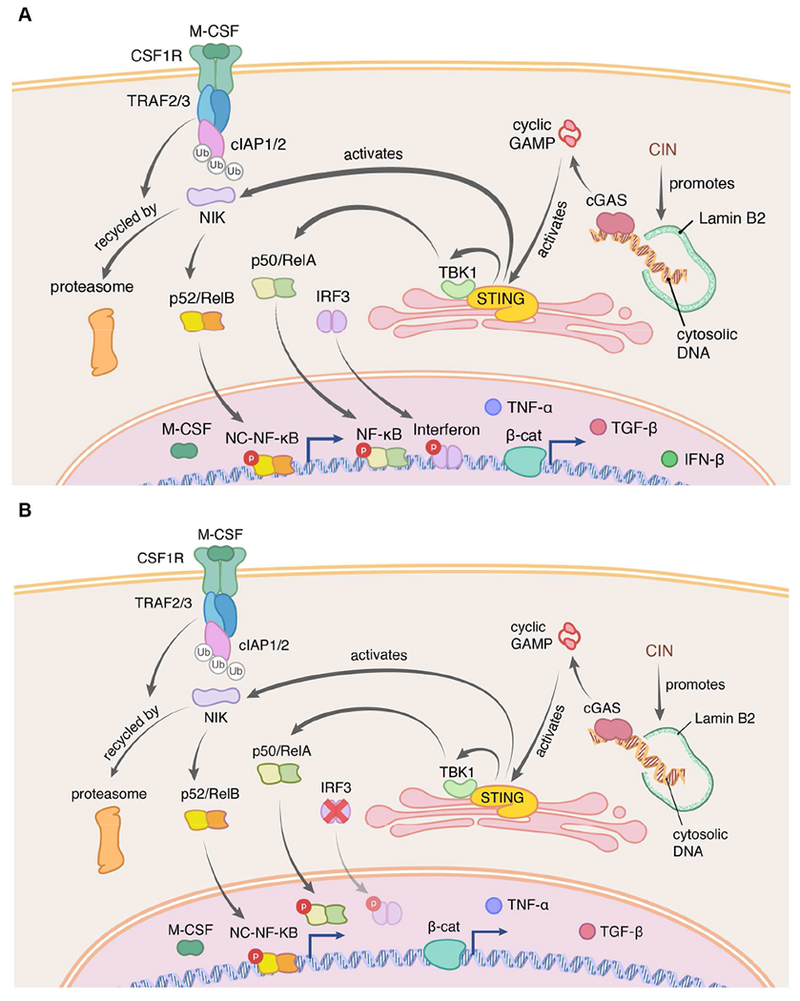
Chromosome segregation errors lead to the formation of micronuclei, which often rupture in S-phase exposing double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) to the cytosol. The presence of cytosolic dsDNA activates the anti-viral cGAS-STING pathway which in normal cells promotes type I interferon production (A). Chromosomally unstable cancer cells however largely suppress type I interferon signaling through multiple mechanisms, yet they maintain the ability to exhibit alternative inflammatory STING-dependent signaling such as NF-κB (B). Chronic NF-κB activation has been shown to mediate the senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP) as well as cellular migration and metastasis.
