Figure 2: Material Characterization of PEG/Collagen IPNs.
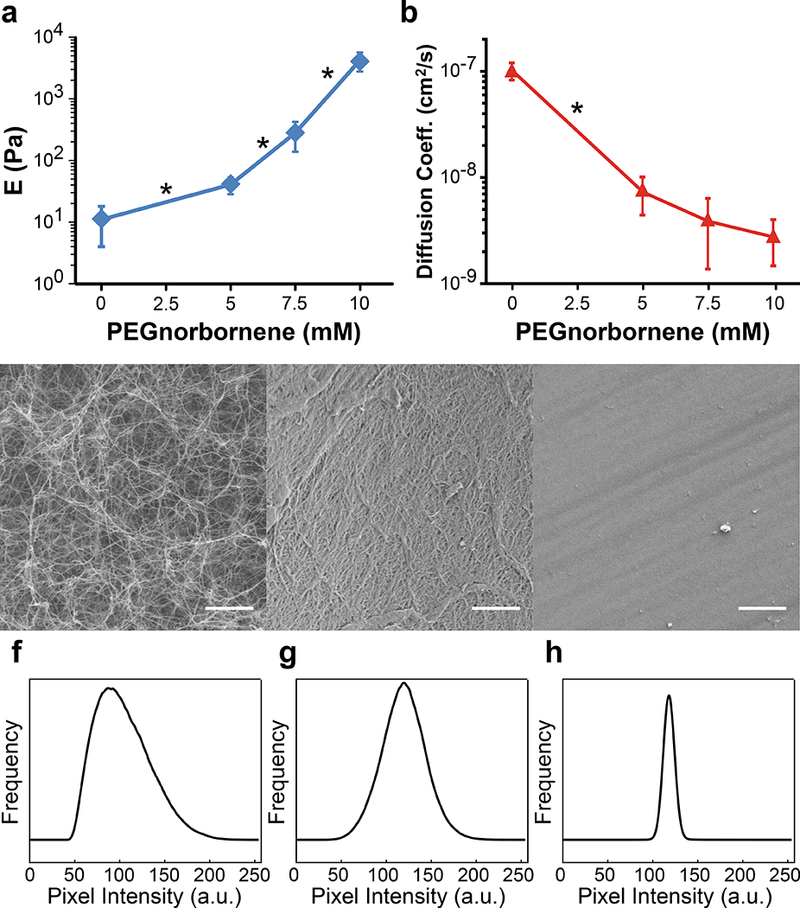
a) Mechanical testing revealed the elastic moduli of PEG/Collagen IPNs spans several orders of magnitude from ~10 Pa to ~4 kPa. b) The diffusion coefficients of BSA-AlexaFluor 594 within PEG/Collagen IPNs, as calculated by the semi-infinite slab approximation, demonstrates that the secondary PEG network hinders biomolecular transport. The microstructures of the IPN system were investigated using SEM imaging, and representative images of the c) collagen-only, d) PEG/Collagen IPN with 10 mM PEG4NB, and e) PEG-only gels with 10 mM PEG4NB are shown. Histogram of pixel intensity for f) collagen-only, g) PEG/Collagen IPN, and h) PEG-only gels is also shown. The left-shifted curve in the histogram for the pure collagen condition reflects its highly porous microstructure, while the more normalized curve in the PEG/collagen IPN histogram is indicative of the secondary PEG network interpenetrating the porous collagen network. Data presented as mean ± SD; n = 3. P value determined using ANOVA with Tukey-Kramer post hoc analysis (*P < 0.001).
